Prognostic roles of the transcriptional expression of exportins in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31371628
- PMCID: PMC6702357
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20190827
Prognostic roles of the transcriptional expression of exportins in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
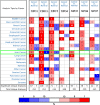
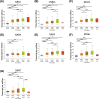
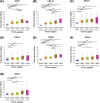
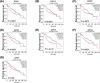
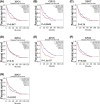
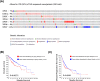
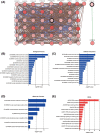
Aims: A large number of studies have suggested that exportins (XPOs) play a pivotal role in human cancers. In the present study, we analyzed XPO mRNA expression in cancer tissues and explored their prognostic value in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).Methods: Transcriptional and survival data related to XPO expression in HCC patients were obtained through the ONCOMINE and UALCAN databases. Survival analysis plots were drawn with Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA). Sequence alteration data for XPOs were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and c-BioPortal. Gene functional enrichment analyses were performed with Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID).Results: Compared with normal liver tissues, significant XPO mRNA overexpression was observed in HCC cancer tissues. There was a trend of higher XPO expression in more advanced clinical stages and lower differentiated pathological grades of HCC. In HCC patients, high expression of XPO1, CSE1L, XPOT, XPO4/5/6 was related to poor overall survival (OS), and XPO1, CSE1L and XPO5/6 were correlated with poor disease-free survival (DFS). The main genetic alterations in XPOs involved mRNA up-regulation, DNA amplification and deletion. General XPO mutations were remarkably associated with worse OS and mostly affected the pathways of RNA transport and oocyte meiosis.Conclusion: High expression of XPOs was associated with a poor prognosis in HCC patients. XPOs may be exploited as good prognostic biomarkers for survival in HCC patients.
Keywords: Exportin; GEPIA; Hepatocellular carcinoma; ONCOMINE; Prognosis.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All datasets used in the present study were retrieved from published literature, and written informed consent was obtained. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University for Human Study and conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of EWSR1 (Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1/EWS RNA binding protein 1) predicts poor survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):7941-7949. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1982844. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34612781 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of X-Ray Repair Cross-Complementing Family Members as Potential Biomarkers for Predicting Progression and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Mar 17;2020:5751939. doi: 10.1155/2020/5751939. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32258128 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional analysis of the expression, prognostic value and immune infiltration activities of the COMMD protein family in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Sep 7;21(1):1001. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08699-3. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34493238 Free PMC article.
-
High HBXIP expression is related to poor prognosis in HCC by extensive database interrogation.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Oct;25(20):6196-6207. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202110_26990. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34730200
-
The association of HMGB1 expression with clinicopathological significance and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis and literature review.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 30;9(10):e110626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110626. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25356587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Role and Clinical Value of PPP2CA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021 Oct 28;9(5):661-671. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00168. Epub 2021 May 13. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34722181 Free PMC article.
-
A Key mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA Competing Endogenous RNA Triple Sub-network Linked to Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 17;10:340. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00340. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32257949 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the value of RAB family genes in prognosis of breast invasive carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2020 May 29;40(5):BSR20201103. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201103. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32432324 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear export protein XPO1 provides a peptide ligand for natural killer cells.Sci Adv. 2024 Aug 23;10(34):eado6566. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ado6566. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39178254 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothionein-3 is a multifunctional driver that modulates the development of sorafenib-resistant phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Biomark Res. 2024 Apr 9;12(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00584-y. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 38594765 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

