Immune Resistance and EGFR Antagonists in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 31370270
- PMCID: PMC6721348
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11081089
Immune Resistance and EGFR Antagonists in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
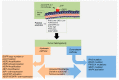
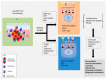
: Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) either alone or in combination with chemotherapy in patients with RAS wild type metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) has revolutionized the treatment of CRC, but with less results than initially envisaged. In recent years, the discovery of multiple pathways leading to the escape from anti-EGFR therapy has revealed an enormous complexity and heterogeneity of human CRC due to the intrinsic genomic instability and immune/cancer cell interaction. Therefore, understanding the mechanistic basis of acquired resistance to targeted therapies represents a major challenge to improve the clinical outcomes of patients with CRC. The latest findings strongly suggest that complex molecular alterations coupled with changes of the immune tumor microenvironment may substantially contribute to the clinical efficacy of EGFR antagonist. In this review, we discuss the most recent findings that contribute to both primary and acquired anti-EGFR therapy resistance. In addition, we analyze how strategies aiming to enhance the favorable effects in the tumor microenvironment may contribute to overcome resistance to EGFR therapies.
Keywords: EGFR; colorectal cancer; immune microenvironment; resistance; targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer: underlying mechanisms and reversal strategies.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 18;40(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02130-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34663410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dissection of effector mechanisms of RAS-mediated resistance to anti-EGFR antibody therapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):45898-45917. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17438. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28507280 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 17;8(3):3980-4000. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14012. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28002810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Strategies in Diseases of the Digestive Tract - 2015 and Beyond Targeted Therapies in Colon Cancer Today and Tomorrow.Dig Dis. 2016;34(5):574-9. doi: 10.1159/000445267. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Dig Dis. 2016. PMID: 27332557
-
Therapeutic value of EGFR inhibition in CRC and NSCLC: 15 years of clinical evidence.ESMO Open. 2016 Sep 16;1(5):e000088. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2016-000088. eCollection 2016. ESMO Open. 2016. PMID: 27843640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improving selection of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer to benefit from cetuximab based on KIR genotypes.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Apr;9(4):e001705. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001705. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33833048 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Suppressing the KIF20A/NUAK1/Nrf2/GPX4 signaling pathway induces ferroptosis and enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Mar 26;13(10):13515-13534. doi: 10.18632/aging.202774. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33819186 Free PMC article.
-
Primary tumor type prediction based on US nationwide genomic profiling data in 13,522 patients.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Jul 26;21:3865-3874. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.07.036. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37593720 Free PMC article.
-
4-Acetyl-Antroquinonol B Improves the Sensitization of Cetuximab on Both Kras Mutant and Wild Type Colorectal Cancer by Modulating the Expression of Ras/Raf/miR-193a-3p Signaling Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 14;22(14):7508. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147508. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299137 Free PMC article.
-
Krill oil supplementation reduces the growth of CT-26 orthotopic tumours in Balb/c mice.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Feb 4;22(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03521-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35120511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sartore-Bianchi A., Siena S., Tonini G., Bardelli A., Santini D. Overcoming dynamic molecular heterogeneity in metastatic colorectal cancer: Multikinase inhibition with regorafenib and the case of rechallenge with anti-EGFR. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;51:54–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.10.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

