Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 31369575
- PMCID: PMC6675055
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220178
Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Our objective was to compare the cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab and other biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) in rheumatoid arthritis using a network meta-analysis (NMA).
Methods: A systematic literature search through May 2018 identified randomized controlled trials (RCT) or observational studies (cohort only) reporting cardiovascular outcomes of tocilizumab (TCZ) and/or abatacept (ABA) and/or rituximab (RTX) and/or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) in rheumatoid arthritis patients. The composite primary outcome was the rate of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes (MACE, myocardial infarction (MI), peripheral artery disease (PAD) and cardiac heart failure (CHF)).
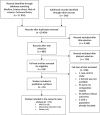
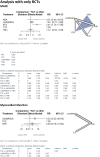
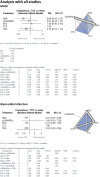
Results: 19 studies were included in the NMA, including 11 RCTs and 8 cohort studies. We found less events with RTX (5.41 [1.70;17.26]. We found no difference between TCZ and other treatments. Concerning MI, we found no difference between TCZ and csDMARD (4.23 [0.22;80.64]), no difference between TCZ and TNFi (2.00 [0.18;21.84]). There was no difference between TCZ and csDMARD (1.51[0.02;103.50] and between TCZ and TNFi (1.00 [0.06;15.85]) for stroke event. With cohorts and RCT NMA, we found no difference between TCZ and other treatments for MACE (0.66 [0.42;1.03] with ABA, 1.04 [0.60;1.81] with RTX, 0.78[0.53;1.16] and 0.91 [0.54;1.51] with csDMARD), but the risk of myocardial infarction was lower with TCZ compared to ABA (0.67 [0.47;0.97]). We lacked data to compare TCZ and other bDMARD for stoke and MI. Not enough data was available to perform a NMA for CHF and PAD.
Conclusions: Despite an increase in cholesterol levels, TCZ has safe cardiovascular outcomes compared to other bDMARD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Malignant Neoplasms in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated With Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors, Tocilizumab, Abatacept, or Rituximab in Clinical Practice: A Nationwide Cohort Study From Sweden.JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Nov 1;177(11):1605-1612. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.4332. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28975211 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Safety of Tocilizumab Versus Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multi-Database Cohort Study.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Jun;69(6):1154-1164. doi: 10.1002/art.40084. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28245350 Free PMC article.
-
Tocilizumab and rituximab have similar effectiveness and are both superior to a second tumour necrosis factor inhibitor in rheumatoid arthritis patients who discontinued a first TNF inhibitor.Acta Reumatol Port. 2019 Apr-Jun;44(2):103-113. Acta Reumatol Port. 2019. PMID: 31243259 English.
-
Biologic or tofacitinib monotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis in people with traditional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) failure: a Cochrane Systematic Review and network meta-analysis (NMA).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 17;11(11):CD012437. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012437. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27855242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rheumatoid factor as predictor of response to abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Aug;43(1):9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2012.11.007. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23290690 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin 6 and Development of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in the General Population.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Jun;10(11):e018549. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018549. Epub 2021 May 17. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33998283 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Considerations in Treating Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020 May;75(5):359-367. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000836. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32282502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adverse effects, pharmacological interactions, and cardiovascular drugs in COVID-19 treatment.Arch Cardiol Mex. 2021 Dec 20;91(Suplemento COVID):079-085. doi: 10.24875/ACM.20000234. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2021. PMID: 33459727 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Tocilizumab in COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;60(9):1131-1146. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1693. Epub 2020 Jul 27. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32557541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Inflammatory Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Development of Atherosclerosis: A Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Aug 26;59(9):1550. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091550. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37763669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76: 960–977. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

