MEK Inhibition Modulates Cytokine Response to Mediate Therapeutic Efficacy in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 31362929
- PMCID: PMC6881545
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0698
MEK Inhibition Modulates Cytokine Response to Mediate Therapeutic Efficacy in Lung Cancer
Abstract
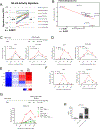
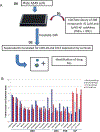
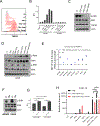
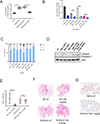
Activating mutations in BRAF, a key mediator of RAS signaling, are present in approximately 50% of melanoma patients. Pharmacologic inhibition of BRAF or the downstream MAP kinase MEK is highly effective in treating BRAF-mutant melanoma. In contrast, RAS pathway inhibitors have been less effective in treating epithelial malignancies, such as lung cancer. Here, we show that treatment of melanoma patients with BRAF and MEK inhibitors (MEKi) activated tumor NF-κB activity. MEKi potentiated the response to TNFα, a potent activator of NF-κB. In both melanoma and lung cancer cells, MEKi increased cell-surface expression of TNFα receptor 1 (TNFR1), which enhanced NF-κB activation and augmented expression of genes regulated by TNFα and IFNγ. Screening of 289 targeted agents for the ability to increase TNFα and IFNγ target gene expression demonstrated that this was a general activity of inhibitors of MEK and ERK kinases. Treatment with MEKi led to acquisition of a novel vulnerability to TNFα and IFNγ-induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells that were refractory to MEKi killing and augmented cell-cycle arrest. Abolishing the expression of TNFR1 on lung cancer cells impaired the antitumor efficacy of MEKi, whereas the administration of TNFα and IFNγ in MEKi-treated mice enhanced the antitumor response. Furthermore, immunotherapeutics known to induce expression of these cytokines synergized with MEKi in eradicating tumors. These findings define a novel cytokine response modulatory function of MEKi that can be therapeutically exploited. SIGNIFICANCE: Lung cancer cells are rendered sensitive to MEK inhibitors by TNFα and IFNγ, providing a strong mechanistic rationale for combining immunotherapeutics, such as checkpoint blockers, with MEK inhibitor therapy for lung cancer.See related commentary by Havel, p. 5699.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
MEK Inhibitors in Lung Cancer-You Can Teach an Old Drug New Tricks.Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 15;79(22):5699-5701. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2590. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31772071
Comment on
-
MEK Inhibitors in Lung Cancer-You Can Teach an Old Drug New Tricks.Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 15;79(22):5699-5701. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2590. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31772071
Similar articles
-
ER Translocation of the MAPK Pathway Drives Therapy Resistance in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma.Cancer Discov. 2019 Mar;9(3):396-415. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0348. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30563872 Free PMC article.
-
BRAF and MEK Inhibitors Increase PD-1-Positive Melanoma Cells Leading to a Potential Lymphocyte-Independent Synergism with Anti-PD-1 Antibody.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jul 15;24(14):3377-3385. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1914. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29650750
-
Upstream mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway inhibition: MEK inhibitor followed by a BRAF inhibitor in advanced melanoma patients.Eur J Cancer. 2014 Jan;50(2):406-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.09.014. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24183461
-
Immunomodulatory effects of BRAF and MEK inhibitors: Implications for Melanoma therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Oct;136:151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30145328 Review.
-
MEK in cancer and cancer therapy.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Feb;141(2):160-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24121058 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer cell-intrinsic expression of MHC II in lung cancer cell lines is actively restricted by MEK/ERK signaling and epigenetic mechanisms.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Apr;8(1):e000441. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000441. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32312906 Free PMC article.
-
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced interferon response positively associates with clinical response in EGFR-mutant lung cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021 May 17;5(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41698-021-00181-4. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34001994 Free PMC article.
-
Combined MEK and JAK/STAT3 pathway inhibition effectively decreases SHH medulloblastoma tumor progression.Commun Biol. 2022 Jul 14;5(1):697. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03654-9. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35835937 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Directly Modulate T Cell Gene Expression and Signaling and Promote Development of Effector-Exhausted T Cells in Murine Tumors.J Immunol. 2024 Feb 15;212(4):737-747. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300475. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38169329
-
Combination IFNβ and Membrane-Stable CD40L Maximize Tumor Dendritic Cell Activation and Lymph Node Trafficking to Elicit Systemic T-cell Immunity.Cancer Immunol Res. 2023 Apr 3;11(4):466-485. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0927. Cancer Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 36757308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao Y, Adjei AA. The clinical development of MEK inhibitors. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2014;11:385–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

