Pathophysiological Role of Caveolae in Hypertension
- PMID: 31355199
- PMCID: PMC6635557
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00153
Pathophysiological Role of Caveolae in Hypertension
Abstract
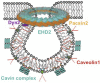
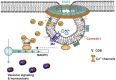
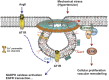
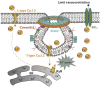
Caveolae, flask-shaped cholesterol-, and glycosphingolipid-rich membrane microdomains, contain caveolin 1, 2, 3 and several structural proteins, in particular Cavin 1-4, EHD2, pacsin2, and dynamin 2. Caveolae participate in several physiological processes like lipid uptake, mechanosensitivity, or signaling events and are involved in pathophysiological changes in the cardiovascular system. They serve as a specific membrane platform for a diverse set of signaling molecules like endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), and further maintain vascular homeostasis. Lack of caveolins causes the complete loss of caveolae; induces vascular disorders, endothelial dysfunction, and impaired myogenic tone; and alters numerous cellular processes, which all contribute to an increased risk for hypertension. This brief review describes our current knowledge on caveolae in vasculature, with special focus on their pathophysiological role in hypertension.
Keywords: Ca2+ channels; caveolae; caveolin 1; endothelial nitric oxide synthase; hypertension.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase targeting to caveolae. Specific interactions with caveolin isoforms in cardiac myocytes and endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 1996 Sep 13;271(37):22810-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.37.22810. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8798458
-
Caveolae, caveolin and control of vascular tone: nitric oxide (NO) and endothelium derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) regulation.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;60 Suppl 4:105-9. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20083858 Review.
-
Caveolae, caveolins, cavins, and endothelial cell function: new insights.Front Physiol. 2012 Jan 6;2:120. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2011.00120. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22232608 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing effects of reactive oxygen species and cholesterol on endothelial nitric oxide synthase and endothelial cell caveolae.Circ Res. 1999 Jul 9;85(1):29-37. doi: 10.1161/01.res.85.1.29. Circ Res. 1999. PMID: 10400908
-
The Caveolin genes: from cell biology to medicine.Ann Med. 2004;36(8):584-95. doi: 10.1080/07853890410018899. Ann Med. 2004. PMID: 15768830 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynein regulates Kv7.4 channel trafficking from the cell membrane.J Gen Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;153(3):e202012760. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202012760. J Gen Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33533890 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of S-Glutathionylation in Health and Disease: A Bird's Eye View.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 18;16(16):2753. doi: 10.3390/nu16162753. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Cardiovascular Biomarker Discovery.Biomedicines. 2020 Nov 30;8(12):552. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8120552. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33265898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Glycocalyx and Caveolae in Vascular Homeostasis and Diseases.Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 13;11:620840. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.620840. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33519523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age attenuates the T-type CaV 3.2-RyR axis in vascular smooth muscle.Aging Cell. 2020 Apr;19(4):e13134. doi: 10.1111/acel.13134. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 32187825 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

