Time-Resolved Small RNA Sequencing Unravels the Molecular Principles of MicroRNA Homeostasis
- PMID: 31350118
- PMCID: PMC6713562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.018
Time-Resolved Small RNA Sequencing Unravels the Molecular Principles of MicroRNA Homeostasis
Abstract
Argonaute-bound microRNAs silence mRNA expression in a dynamic and regulated manner to control organismal development, physiology, and disease. We employed metabolic small RNA sequencing for a comprehensive view on intracellular microRNA kinetics in Drosophila. Based on absolute rate of biogenesis and decay, microRNAs rank among the fastest produced and longest-lived cellular transcripts, disposing up to 105 copies per cell at steady-state. Mature microRNAs are produced within minutes, revealing tight intracellular coupling of biogenesis that is selectively disrupted by pre-miRNA-uridylation. Control over Argonaute protein homeostasis generates a kinetic bottleneck that cooperates with non-coding RNA surveillance to ensure faithful microRNA loading. Finally, regulated small RNA decay enables the selective rapid turnover of Ago1-bound microRNAs, but not of Ago2-bound small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), reflecting key differences in the robustness of small RNA silencing pathways. Time-resolved small RNA sequencing opens new experimental avenues to deconvolute the timescales, molecular features, and regulation of small RNA silencing pathways in living cells.
Keywords: Argonaute; RNA expression dynamics; RNA metabolism; metabolic RNA labeling; microRNAs; post-transcriptional gene regulation; small RNA homeostasis; small RNA silencing; time-resolved RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
VAH, BR and SLA declare competing financial interest. A patent application related to this work has been filed.
Figures
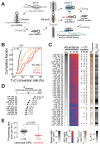
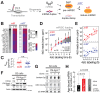
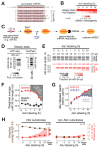
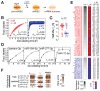

Comment in
-
Insights into the kinetics of microRNA biogenesis and turnover.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;20(9):511. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0164-9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31366986 No abstract available.
-
Toward a Comprehensive View of MicroRNA Biology.Mol Cell. 2019 Aug 22;75(4):666-668. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.001. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31442421
Similar articles
-
The small RNA landscape is stable with age and resistant to loss of dFOXO signaling in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 16;17(11):e0273590. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273590. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36383505 Free PMC article.
-
The 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease Nibbler shapes the 3' ends of microRNAs bound to Drosophila Argonaute1.Curr Biol. 2011 Nov 22;21(22):1878-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.09.034. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 22055293 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting of Drosophila small silencing RNAs.Cell. 2007 Jul 27;130(2):299-308. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.057. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17662944 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly and function of small RNA - argonaute protein complexes.Biol Chem. 2014 Jun;395(6):611-29. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0116. Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24603840 Review.
-
Argonaute proteins: functional insights and emerging roles.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Jul;14(7):447-59. doi: 10.1038/nrg3462. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23732335 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of microRNAs in Ovarian Cancer Tumorigenesis: Two Decades Later, What Have We Learned?Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 21;10:1084. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01084. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32850313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To kill a microRNA: emerging concepts in target-directed microRNA degradation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 28;52(4):1558-1574. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae003. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38224449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The developmentally timed decay of an essential microRNA family is seed-sequence dependent.Cell Rep. 2022 Aug 9;40(6):111154. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111154. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35947946 Free PMC article.
-
A maternally programmed intergenerational mechanism enables male offspring to make piRNAs from Y-linked precursor RNAs in Drosophila.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Oct;25(10):1495-1505. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01227-4. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37723298 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Nutrient-Mediated Regulation of MicroRNAs in Pancreatic β-cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 4;12:704824. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.704824. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34803905 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

