The protective effects of bone mesenchymal stem cells on paraquat-induced acute lung injury via the muc5b and ERK/MAPK signaling pathways
- PMID: 31312382
- PMCID: PMC6614636
The protective effects of bone mesenchymal stem cells on paraquat-induced acute lung injury via the muc5b and ERK/MAPK signaling pathways
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the protective effect of bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) on paraquat (PQ)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) and investigate the possible underlying mechanisms.
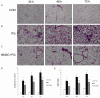
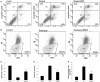
Methods: Male Sprague Dawley rats were treated with BMSCs (3 × 106) 1 h after intraperitoneal injection of PQ. The cell apoptosis rate and mitochondrial membrane potential in rat pulmonary alveolar type II epithelial (ATII) cells were quantitated by flow cytometry. IL-17, IL-6, and MUC5B levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and ATII culture medium were measured. Lung tissues were collected to determine the wet-to-dry (W/D) ratios and lung injury scores, in addition to the protein and mRNA expression levels of ERK1/2, Bcl-2, Bax, and muc5b.
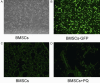
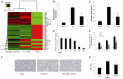
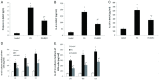
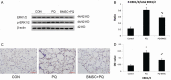
Results: BMSCs had decreased mRNA expression of Muc5b in lung tissue of rats with PQ-induced ALI as shown by RNA-seq. Treatment with BMSCs also alleviated the PQ-induced increases in protein expression in the BALF and reduced the concentration of IL-17, IL-6, and Muc5b in both the BALF and ATII culture medium. In addition, the ATII cell apoptosis rate and mitochondrial membrane potential, as well as the W/D ratios, were decreased by BMSC treatment. Moreover, BMSCs ameliorated the expression levels of Bax mRNA and active caspase-3 proteins and increased Bcl-2 mRNA expression. Furthermore, BMSCs attenuated ERK1/2 activation upon PQ-induced ALI in lung tissue.
Conclusion: BMSC therapy can protect against PQ-induced ALI in rats. A possible mechanism is the suppression of the muc5b and ERK/MAPK signaling pathways, resulting in an improvement in the endothelial permeability and a decrease in inflammation and cell apoptosis.
Keywords: Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells; Muc5b and ERK/MAPK signaling pathways; acute lung injury; paraquat poisoning.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Optimal conditions of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on paraquat-induced acute lung injury in rats].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Sep;30(9):645-9. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23257085 Chinese.
-
Protective effects of SOD2 overexpression in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on lung injury induced by acute paraquat poisoning in rats.Life Sci. 2018 Dec 1;214:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.020. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30321544
-
The MUC5B Mucin Is Involved in Paraquat-Induced Lung Inflammation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jul 16;2020:7028947. doi: 10.1155/2020/7028947. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32724493 Free PMC article.
-
[The protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells carrying antioxidant gene superoxide dismutase on paraquat lung injury in mice].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2016 Jan;34(1):1-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2016.01.001. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27014807 Chinese.
-
Klotho Alleviates Lung Injury Caused by Paraquat via Suppressing ROS/P38 MAPK-Regulated Inflammatory Responses and Apoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 May 13;2020:1854206. doi: 10.1155/2020/1854206. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32509139 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of oxidative stress/JNK/ERK signals in paraquat-triggered hepatic apoptosis.Curr Res Toxicol. 2024 Feb 10;6:100155. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2024.100155. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38379848 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced osteoinductivity and corrosion resistance of dopamine/gelatin/rhBMP-2-coated β-TCP/Mg-Zn orthopedic implants: An in vitro and in vivo study.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 30;15(1):e0228247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228247. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31999748 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in pulmonary fibrosis: a meta-analysis of preclinical studies.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Aug 18;12(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02496-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34407861 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for paraquat-induced lung injury.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 13;40(1):70. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09911-3. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39136896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Pancreatic Damage in Rats for Two Methods of Paraquat Administration.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 20;12:611433. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.611433. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33967752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA, Sanchez-Navarro A, Remiao F, Bastos ML, Carvalho F. Paraquat poisonings: mechanisms of lung toxicity, clinical features, and treatment. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008;38:13–71. - PubMed
-
- Gunawardena G, Roberts DM, Buckley NA. Randomized control trial of immunosuppression in paraquat poisoning. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:330–331. - PubMed
-
- Walter J, Ware LB, Matthay MA. Mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms of potential therapeutic benefit in ARDS and sepsis. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2:1016–1026. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
