Sex differences in the association between diabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 5,162,654 participants
- PMID: 31296205
- PMCID: PMC6625042
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-019-1355-0
Sex differences in the association between diabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 5,162,654 participants
Abstract
Background: Studies have suggested sex differences in the mortality rate associated with diabetes. We conducted a meta-analysis to estimate the relative effect of diabetes on the risk of all-cause, cancer, cardiovascular disease (CVD), infectious disease, and respiratory disease mortality in women compared with men.
Methods: Studies published from their inception to April 1, 2018, identified through a systematic search of PubMed and EMBASE and review of references. We used the sex-specific RRs to derive the women-to-men ratio of RRs (RRR) and 95% CIs from each study. Subsequently, the RRR for each outcome was pooled with random-effects meta-analysis weighted by the inverse of the variances of the log RRRs.
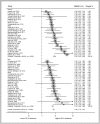
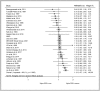
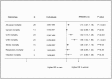
Results: Forty-nine studies with 86 prospective cohorts met the inclusion criteria and were eligible for analysis. The pooled women-to-men RRR showed a 13% greater risk of all-cause mortality associated with diabetes in women than in men (RRR 1.13, 95% CI 1.07 to 1.19; P < 0.001). The pooled multiple-adjusted RRR indicated a 30% significantly greater excess risk of CVD mortality in women with diabetes compared with men (RRR 1.30, 95% CI 1.13 to 1.49; P < 0.001). Compared with men with diabetes, women with diabetes had a 58% greater risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) mortality, but only an 8% greater risk of stroke mortality (RRRCHD 1.58, 95% CI 1.32 to 1.90; P < 0.001; RRRstroke 1.08, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.15; P < 0.001). However, no sex differences were observed in pooled results of populations with or without diabetes for all-cancer (RRR 1.02, 95% CI 0.98 to 1.06; P = 0.21), infectious (RRR 1.13, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.38; P = 0.33), and respiratory mortality (RRR 1.08, 95% CI 0.95 to 1.23; P = 0.26).
Conclusions: Compared with men with the same condition, women with diabetes have a 58% and 13% greater risk of CHD and all-cause mortality, respectively, although there was a significant heterogeneity between studies. This points to an urgent need to develop sex- and gender-specific risk assessment strategies and therapeutic interventions that target diabetes management in the context of CHD prevention.
Keywords: Diabetes; Meta-analysis; Mortality; Sex difference.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex differences in the association between marital status and the risk of cardiovascular, cancer, and all-cause mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 7,881,040 individuals.Glob Health Res Policy. 2020 Feb 28;5:4. doi: 10.1186/s41256-020-00133-8. eCollection 2020. Glob Health Res Policy. 2020. PMID: 32161813 Free PMC article.
-
Association between diabetes mellitus and the risk for major cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in women compared with men: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.BMJ Open. 2019 Jul 17;9(7):e024935. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024935. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31320342 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes mellitus and the risk of gastrointestinal cancer in women compared with men: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 16;18(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4351-4. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29661174 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the relationship between socioeconomic status and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Epidemiol Community Health. 2017 Jun;71(6):550-557. doi: 10.1136/jech-2016-207890. Epub 2016 Dec 14. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2017. PMID: 27974445 Review.
-
Diabetes as a risk factor for heart failure in women and men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 cohorts including 12 million individuals.Diabetologia. 2019 Sep;62(9):1550-1560. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4926-x. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31317230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Do Women with Diabetes Need More Intensive Action for Cardiovascular Reduction than Men with Diabetes?Curr Diab Rep. 2020 Oct 9;20(11):61. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-01348-2. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 33033953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox Regulatory Changes of Circadian Rhythm by the Environmental Risk Factors Traffic Noise and Air Pollution.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Oct;37(10-12):679-703. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0272. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 35088601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-related differences in diabetic kidney disease: A review on the mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications.J Diabetes Complications. 2021 Apr;35(4):107841. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107841. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Diabetes Complications. 2021. PMID: 33423908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences among young individuals with myocardial infarction.Eur Heart J. 2020 Nov 7;41(42):4138-4140. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa682. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 33049781 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sex differences in pathogenesis and treatment of dyslipidemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and steatotic liver disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 23;11:1458025. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1458025. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39376658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioral, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1345–1422. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32366-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases 2013-2020. Available from http://www.who.int/nmh/events/ncd_action_plan/en/. Accessed 9 Dec 2018
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes atlas. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous