iDS372, a Phenotypically Reconciled Model for the Metabolism of Streptococcus pneumoniae Strain R6
- PMID: 31293525
- PMCID: PMC6603136
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01283
iDS372, a Phenotypically Reconciled Model for the Metabolism of Streptococcus pneumoniae Strain R6
Abstract
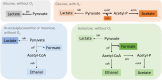
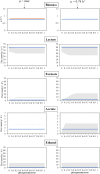
A high-quality GSM model for Streptococcus pneumoniae R6 model strain (iDS372), comprising 372 genes and 529 reactions, was developed. The construction of this model involved performing a genome-wide reannotation to identify the metabolic capacity of the bacterium. A reaction representing the abstraction of the biomass composition was reconciled from several studies reported in the literature and previous models, and included in the model. The final model comprises two compartments and manifold automatically generated gene rules. The validation was performed with experimental data from recent studies, regarding the usability of carbon sources, the effect of the presence of oxygen, and the requirement of amino acids for growth. This model can be used to better understand the metabolism of this major pathogen, provide clues regarding new drug targets, and eventually design strategies for fighting infections by these bacteria.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae R6; avirulent; genome-scale metabolic model; iDS372; metabolic reconstruction; phenotypical reconciliation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome of the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R6.J Bacteriol. 2001 Oct;183(19):5709-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.19.5709-5717.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11544234 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor-kappaB activation in mouse lung lavage cells in response to Streptococcus pneumoniae pulmonary infection.Crit Care Med. 2000 Sep;28(9):3249-56. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200009000-00021. Crit Care Med. 2000. PMID: 11008989
-
Genome sequence of Avery's virulent serotype 2 strain D39 of Streptococcus pneumoniae and comparison with that of unencapsulated laboratory strain R6.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jan;189(1):38-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.01148-06. Epub 2006 Oct 13. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17041037 Free PMC article.
-
Infection and metabolism - Streptococcus pneumoniae metabolism facing the host environment.Cytokine. 2018 Dec;112:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.07.021. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 30077545 Review.
-
Mosaic genes and mosaic chromosomes-genomic variation in Streptococcus pneumoniae.Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Sep;294(2-3):157-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.06.019. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15493826 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Scale Metabolic Model of the Human Pathogen Candida albicans: A Promising Platform for Drug Target Prediction.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Sep 11;6(3):171. doi: 10.3390/jof6030171. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32932905 Free PMC article.
-
merlin, an improved framework for the reconstruction of high-quality genome-scale metabolic models.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jun 24;50(11):6052-6066. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac459. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35694833 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Validation of a Genome-Scale Metabolic Model of Streptococcus oralis (iCJ415), a Human Commensal and Opportunistic Pathogen.Front Genet. 2020 Mar 3;11:116. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00116. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32194617 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Scale Metabolic Modeling for Unraveling Molecular Mechanisms of High Threat Pathogens.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 3;8:566702. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.566702. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33251208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Genome-Scale Metabolic Model for the Human Pathogen Candida Parapsilosis and Early Identification of Putative Novel Antifungal Drug Targets.Genes (Basel). 2022 Feb 5;13(2):303. doi: 10.3390/genes13020303. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205348 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

