Selective miRNA Modulation Fails to Activate HIV Replication in In Vitro Latency Models
- PMID: 31288207
- PMCID: PMC6614709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.06.006
Selective miRNA Modulation Fails to Activate HIV Replication in In Vitro Latency Models
Abstract
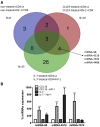
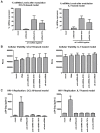
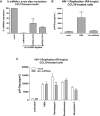
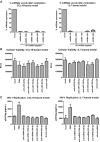
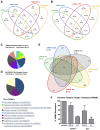
HIV remains incurable because of viral persistence in latent reservoirs that are inaccessible to antiretroviral therapy. A potential curative strategy is to reactivate viral gene expression in latently infected cells. However, no drug so far has proven to be successful in vivo in reducing the reservoir, and therefore new anti-latency compounds are needed. We explored the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in latency maintenance and their modulation as a potential anti-latency strategy. Latency models based on treating resting CD4 T cells with chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 (CCL19) or interleukin-7 (IL7) before HIV infection and next-generation sequencing were used to identify the miRNAs involved in HIV latency. We detected four upregulated miRNAs (miRNA-98, miRNA-4516, miRNA-4488, and miRNA-7974). Individual or combined inhibition of these miRNAs was performed by transfection into cells latently infected with HIV. Viral replication, assessed 72 h after transfection, did not increase after miRNA modulation, despite miRNA inhibition and lack of toxicity. Furthermore, the combined modulation of five miRNAs previously associated with HIV latency was not effective in these models. Our results do not support the modulation of miRNAs as a useful strategy for the reversal of HIV latency. As shown with other drugs, the potential of miRNA modulation as an HIV reactivation strategy could be dependent on the latency model used.
Keywords: CCL19; HIV latency; HIV latency model; IL-7; LRA; latency-reversing agent; miRNA modulation.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maraviroc Is Associated with Latent HIV-1 Reactivation through NF-κB Activation in Resting CD4+ T Cells from HIV-Infected Individuals on Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy.J Virol. 2018 Apr 13;92(9):e01931-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01931-17. Print 2018 May 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29444937 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranscriptional Regulation of HIV-1 Gene Expression during Replication and Reactivation from Latency by Nuclear Matrix Protein MATR3.mBio. 2018 Nov 13;9(6):e02158-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02158-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30425153 Free PMC article.
-
An In-Depth Comparison of Latency-Reversing Agent Combinations in Various In Vitro and Ex Vivo HIV-1 Latency Models Identified Bryostatin-1+JQ1 and Ingenol-B+JQ1 to Potently Reactivate Viral Gene Expression.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jul 30;11(7):e1005063. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005063. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26225566 Free PMC article.
-
Reservoirs for HIV-1: mechanisms for viral persistence in the presence of antiviral immune responses and antiretroviral therapy.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:665-708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.665. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837072 Review.
-
Current Status of Latency Reversing Agents Facing the Heterogeneity of HIV-1 Cellular and Tissue Reservoirs.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 24;10:3060. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03060. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32038533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Micro RNA Targets in HIV Latency: Insights into Novel Layers of Latency Control.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021 Feb;37(2):109-121. doi: 10.1089/AID.2020.0150. Epub 2020 Nov 10. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021. PMID: 33045840 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Latency and Viral Reservoirs: Existing Reversal Approaches and Potential Technologies, Targets, and Pathways Involved in HIV Latency Studies.Cells. 2021 Feb 23;10(2):475. doi: 10.3390/cells10020475. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33672138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HibeRNAtion: HIV-1 RNA Metabolism and Viral Latency.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 14;12:855092. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.855092. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35774399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective miRNA inhibition in CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes enhances HIV-1 specific cytotoxic responses.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 26;13:998368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.998368. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36225912 Free PMC article.
-
The reservoir of latent HIV.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 28;12:945956. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.945956. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35967854 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- UNAIDS . 2017. Fact sheet 2015.https://www.aidsdatahub.org/sites/default/files/publication/UNAIDS_fact_...
-
- Siliciano J.D., Kajdas J., Finzi D., Quinn T.C., Chadwick K., Margolick J.B., Kovacs C., Gange S.J., Siliciano R.F. Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat. Med. 2003;9:727–728. - PubMed
-
- Coiras M., López-Huertas M.R., Pérez-Olmeda M., Alcamí J. Understanding HIV-1 latency provides clues for the eradication of long-term reservoirs. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009;7:798–812. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

