Sesamol Inhibited Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Hyperpigmentation and Damage in C57BL/6 Mouse Skin
- PMID: 31284438
- PMCID: PMC6680965
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox8070207
Sesamol Inhibited Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Hyperpigmentation and Damage in C57BL/6 Mouse Skin
Abstract
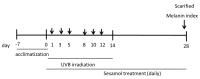
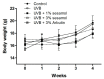
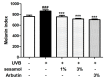
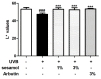
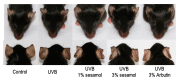
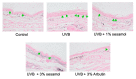
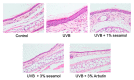
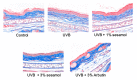
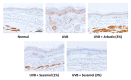
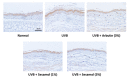
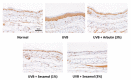
Melanin is synthesized through a series of oxidative reactions initiated with tyrosine and catalyzed by melanogenesis-related proteins such as tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein-1 (TRP-1), dopachrome tautomerase (TRP-2), and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF). Our previous study demonstrated that sesamol inhibited melanin synthesis through the inhibition of the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R)/MITF/tyrosinase pathway in B16F10 cells. In this study, sesamol was applied to C57BL/6 mouse skin to understand its activity with respect to skin pigmentation. The results indicated that ultraviolet (UV) B-induced hyperpigmentation in the C57BL/6 mouse skin was significantly reduced by topical application of sesamol for 4 weeks. Sesamol reduced the melanin index and melanin content of the skin. In addition, sesamol elevated the brightness (L* value) of the skin. Sesamol also reduced UVB-induced hyperplasia of epidermis and collagen degradation in dermis. In immunohistochemical staining, topical application of sesamol reduced UVB-induced tyrosinase, TRP-1, TRP-2, and MITF expression in the epidermis of the skin. These results demonstrated that sesamol is a potent depigmenting agent in the animal model.
Keywords: melanogenesis; microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; sesamol; tyrosinase; tyrosinase-related protein-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Regulating Melanin-Related Signal Transduction in B16F10 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 7;19(4):1108. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041108. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29642438 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation Effect of Radiofrequency Irradiation on UV-B-Induced Skin Pigmentation by Decreasing Melanin Synthesis and through Upregulation of Heat Shock Protein 70.Molecules. 2021 Dec 17;26(24):7648. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247648. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946730 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Pigmentation Effects of Eight Phellinus linteus-Fermented Traditional Crude Herbal Extracts on Brown Guinea Pigs of Ultraviolet B-Induced Hyperpigmentation.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Mar 28;28(3):375-380. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1711.11043. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29316744
-
Discovery of new depigmenting compounds and their efficacy to treat hyperpigmentation: Evidence from in vitro study.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019 Jun;18(3):703-727. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12900. Epub 2019 Mar 13. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30866156 Review.
-
The effect of Vitamin C on melanin pigmentation - A systematic review.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2020 May-Aug;24(2):374-382. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_207_20. Epub 2020 Sep 9. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33456250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SFRP5 inhibits melanin synthesis of melanocytes in vitiligo by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Genes Dis. 2020 Jun 15;8(5):677-688. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.06.003. eCollection 2021 Sep. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 34291139 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Application of No-Ozone Cold Plasma in Combination with Vitamin C Reduced Skin Redness and Pigmentation of UV-Irradiated Mice.Biomedicines. 2023 May 27;11(6):1563. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061563. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371658 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Two Different Methods to Induce Skin Melanin Deposition Models in Guinea Pigs.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Aug 29;16:2341-2356. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S420501. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37663883 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Graphene Oxide Nanoribbon as a Novel Whitening Agent Inhibits Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor-Related Melanogenesis Mechanism.ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 19;5(12):6588-6597. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b04316. eCollection 2020 Mar 31. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32258894 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Sesamin against UVB-Induced Skin Inflammation and Photodamage In Vitro and In Vivo.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 12;9(9):479. doi: 10.3390/biom9090479. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31547364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam M.B., Bajpai V.K., Lee J., Zhao P., Byeon J.H., Ra J.S., Majumder R., Lee J.S., Yoon J.I., Rather I.A., et al. Inhibition of melanogenesis by jineol from Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans via MAP-Kinase mediated MITF downregulation and the proteasomal degradation of tyrosinase. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:45858. doi: 10.1038/srep45858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hearing V.J., Jr. Mammalian monophenol monooxygenase (tyrosinase): Purification, properties, and reactions catalyzed. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:154–165. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

