Probiotics for Alleviating Alcoholic Liver Injury
- PMID: 31263495
- PMCID: PMC6556793
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9097276
Probiotics for Alleviating Alcoholic Liver Injury
Abstract
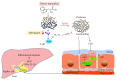
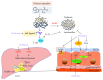
Many animal experiments and clinical trials showed that probiotics are effective for the treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol disrupts the composition of intestinal flora; probiotics modulate the gut microbiota and reverse alcohol-associated intestinal barrier dysfunction by decreasing intestinal mucosal permeability and preventing intestinal bacteria from translocating. Probiotics enhance immune responses and reduce the levels of alcohol-induced inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in the liver and intestine. Probiotics also increase fatty acid β-oxidation and reduce lipogenesis, combating alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge regarding the mechanism of action of probiotics for reducing the effects of alcoholic liver disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Are Probiotics Effective in Targeting Alcoholic Liver Diseases?Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019 Jun;11(2):335-347. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9419-6. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019. PMID: 29687200
-
Probiotics-Based Treatment as an Integral Approach for Alcohol Use Disorder in Alcoholic Liver Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 24;12:729950. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.729950. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34630107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the potential of probiotics in the treatment of alcoholic liver disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 9;14:1212742. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1212742. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37361234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
-
Role of Probiotics in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Does Gut Microbiota Matter?Nutrients. 2019 Nov 19;11(11):2837. doi: 10.3390/nu11112837. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31752378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus plantarum Lp2 improved LPS-induced liver injury through the TLR-4/MAPK/NFκB and Nrf2-HO-1/CYP2E1 pathways in mice.Food Nutr Res. 2022 Jul 5;66. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v66.5459. eCollection 2022. Food Nutr Res. 2022. PMID: 35903291 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum Alleviate Liver Injury and Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating NF-κB and AMPK Signaling.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 28;34(1):149-156. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2310.10006. Epub 2023 Dec 26. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38105432 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a Single Dose of a Probiotic Nutritional Supplement (AB001) on Absorption of Ethylalcohol: Results From a Randomized Double-Blind Crossover Study.Nutr Metab Insights. 2023 Jan 15;16:11786388221141174. doi: 10.1177/11786388221141174. eCollection 2023. Nutr Metab Insights. 2023. PMID: 36686368 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacterium Longum: Protection against Inflammatory Bowel Disease.J Immunol Res. 2021 Jul 23;2021:8030297. doi: 10.1155/2021/8030297. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34337079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Role of Probiotics Against Environmental-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Mechanisms, Clinical Perspectives, Limitations, and Future.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Sep 24. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10365-6. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39316257 Review.
References
-
- Chávez-Tapia N. C., González-Rodríguez L., Jeong M. S., et al. Current evidence on the use of probiotics in liver diseases. Journal of Functional Foods. 2015;17:137–151. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.05.009. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

