Tracking knowledge evolution, hotspots and future directions of emerging technologies in cancers research: a bibliometrics review
- PMID: 31258772
- PMCID: PMC6584937
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.32739
Tracking knowledge evolution, hotspots and future directions of emerging technologies in cancers research: a bibliometrics review
Abstract
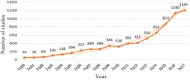
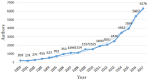
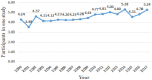
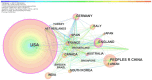
Due to various environmental pollution issues, cancers have become the "first killer" of human beings in the 21st century and their control has become a global strategy of human health. The increasing development of emerging information technologies has provided opportunities for prevention, early detection, diagnosis, intervention, prognosis, nursing, and rehabilitation of cancers. In recent years, the literature associated with emerging technologies in cancer has grown rapidly, but few studies have used bibliometrics and a visualization approach to conduct deep mining and reveal a panorama of this field. To explore the dynamic knowledge evolution of emerging information technologies in cancer literature, we comprehensively analyzed the development status and research hotspots in this field from bibliometrics perspective. We collected 7,136 articles (2000-2017) from the Web of Science database and visually displayed the dynamic knowledge evolution process via the analysis on time-sequence changes, spatial distribution, knowledge base, and hotspots. Much institutional cooperation occurs in this field, and research groups are relatively concentrated. BMC Bioinformatics, PLOS One, Journal of Urology, Scientific Reports, and Bioinformatics are the top five journals in this field. Research hotspots are mainly concentrated in two dimensions: the disease dimension (e.g., cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer), and the technical dimension (e.g., robotics, machine learning, data mining, and etc.). The emerging technologies in cancer research is fast ascending and promising. This study also provides researchers with panoramic knowledge of this field, as well as research hotspots and future directions.
Keywords: bibliometrics; cancers; emerging information technology; hotspots; knowledge evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Visualizing the knowledge structure and evolution of big data research in healthcare informatics.Int J Med Inform. 2017 Feb;98:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Int J Med Inform. 2017. PMID: 28034409 Review.
-
Visualizing the intellectual structure and evolution of electronic health and telemedicine research.Int J Med Inform. 2019 Oct;130:103947. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.08.007. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Int J Med Inform. 2019. PMID: 31450080
-
Knowledge mapping analysis of international research on environmental communication using bibliometrics.J Environ Manage. 2021 Nov 15;298:113475. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113475. Epub 2021 Aug 6. J Environ Manage. 2021. PMID: 34365181 Review.
-
Exploring emerging IoT technologies in smart health research: a knowledge graph analysis.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020 Oct 8;20(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12911-020-01278-9. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020. PMID: 33032598 Free PMC article.
-
CiteSpace-based Document Information Visualization of Literature Published by Journal of Forensic Medicine from 1985 to 2018.Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Aug;35(4):423-427. doi: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 Aug 25. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31532150 Chinese, English.
Cited by
-
The top 100 most cited papers on endometrial carcinoma: A bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 18;12:987980. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.987980. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36059668 Free PMC article.
-
Data Mining in Healthcare: Applying Strategic Intelligence Techniques to Depict 25 Years of Research Development.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 17;18(6):3099. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063099. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33802880 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots for pediatric fractures from 2017 to 2022: A bibliometric and visual analysis via Citespace.J Child Orthop. 2023 Dec 14;18(1):40-48. doi: 10.1177/18632521231217333. eCollection 2024 Feb. J Child Orthop. 2023. PMID: 38348436 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge mapping of targeted immunotherapy for myasthenia gravis from 1998 to 2022: A bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 29;13:998217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.998217. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36248874 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends on traditional Chinese medicine and acute pancreatitis: A bibliometric analysis from 2007 to mid-2023.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 15;10(5):e25659. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25659. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38455538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Vries E, De Poll-Franse V, Louwman W J. et al. Predictions of skin cancer incidence in the Netherlands up to 2015. British Journal of Dermatology. 2005;152(3):481–488. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan R, Badwe R A, Rath G K. et al. Cancer research in India: national priorities, global results. The Lancet Oncology. 2014;15(6):e213–e222. - PubMed
-
- Lynch C. Big data: How do your data grow? Nature. 2008;455(7209):28. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

