RNA-seq analysis of blood of valproic acid-responsive and non-responsive pediatric patients with epilepsy
- PMID: 31258675
- PMCID: PMC6566089
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7538
RNA-seq analysis of blood of valproic acid-responsive and non-responsive pediatric patients with epilepsy
Abstract
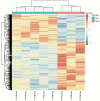
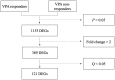
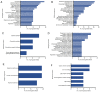
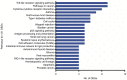
Epilepsy is the most common chronic neurological disorder, affecting ~70 million individuals worldwide. However, approximately one-third of the patients are refractory to epilepsy medication. Of note, 100% of patients with genetic epilepsy who are resistant to the traditional drug, valproic acid (VPA), are also refractory to the other anti-epileptic drugs. The aim of the present study was to compare the transcriptomes in VPA responders and non-responders, to explore the mechanism of action of VPA and identify possible biomarkers to predict VPA resistance. Thus, RNA-seq was employed for transcriptomic analysis, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were analyzed using Cuffdiff software and the DAVID database was used to infer the functions of the DEGs. A protein-protein interaction network was obtained using STRING and visualized with Cytoscape. A total of 389 DEGs between VPA-responsive and non-responsive pediatric patients were identified. Of these genes, 227 were upregulated and 162 were downregulated. The upregulated DEGs were largely associated with cytokines, chemokines and chemokine receptor-binding factors, whereas the downregulated DEGs were associated with cation channels, iron ion binding proteins, and immunoglobulin E receptors. In the pathway analysis, the toll-like receptor signaling pathway, pathways in cancer, and cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction were mostly enriched by the DEGs. Furthermore, three modules were identified by protein-protein interaction analysis, and the potential hub genes, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 and 4, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β, which are known to be closely associated with epilepsy, were identified. These specific chemokines may participate in processes associated with VPA resistance and may be potential biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of VPA.
Keywords: RNA-seq; biomarkers; efficacy; valproic acid.
Figures

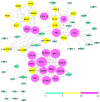
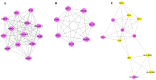
Similar articles
-
Identification of mRNA expression biomarkers associated with epilepsy and response to valproate with co-expression analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 18;13:1019121. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1019121. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36330432 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Homer1b/c induces valproic acid resistance in epilepsy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Jan;29(1):331-343. doi: 10.1111/cns.14008. Epub 2022 Nov 9. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 36353757 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate genes and pathways associated with brain metastasis from lung cancer compared with lymph node metastasis.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Aug;18(2):1276-1284. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7712. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31363372 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of genes associated with prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma based on GEO and TCGA databases.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 May;99(19):e20183. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020183. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32384511 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of candidate biomarkers and pathways associated with SCLC by bioinformatics analysis.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):1538-1550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9095. Epub 2018 May 29. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29845250 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic insights into GABAergic development in Dravet Syndrome iPSC and therapeutic implications.Elife. 2024 Aug 27;12:RP92599. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92599. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39190448 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analysis of Expression Profile and Potential Pathogenic Mechanism of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy With Hippocampal Sclerosis.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 16;16:892022. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.892022. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35784838 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-221-3p Suppresses the Microglia Activation and Seizures by Inhibiting of HIF-1α in Valproic Acid-Resistant Epilepsy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 23;12:714556. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.714556. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34497517 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mRNA expression biomarkers associated with epilepsy and response to valproate with co-expression analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 18;13:1019121. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1019121. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36330432 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Homer1b/c induces valproic acid resistance in epilepsy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Jan;29(1):331-343. doi: 10.1111/cns.14008. Epub 2022 Nov 9. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 36353757 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
