RNA delivery biomaterials for the treatment of genetic and rare diseases
- PMID: 31255978
- PMCID: PMC6635005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119291
RNA delivery biomaterials for the treatment of genetic and rare diseases
Abstract
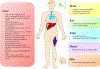
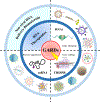
Genetic and rare diseases (GARDs) affect more than 350 million patients worldwide and remain a significant challenge in the clinic. Hence, continuous efforts have been made to bridge the significant gap between the supply and demand of effective treatments for GARDs. Recent decades have witnessed the impressive progress in the fight against GARDs, with an improved understanding of the genetic origins of rare diseases and the rapid development in gene therapy providing a new avenue for GARD therapy. RNA-based therapeutics, such as RNA interference (RNAi), messenger RNA (mRNA) and RNA-involved genome editing technologies, demonstrate great potential as a therapy tool for treating genetic associated rare diseases. In the meantime, a variety of RNA delivery vehicles were established for boosting the widespread applications of RNA therapeutics. Among all the RNA delivery platforms which enable the systemic applications of RNAs, non-viral RNA delivery biomaterials display superior properties and a few biomaterials have been successfully exploited for achieving the RNA-based gene therapies on GARDs. In this review article, we focus on recent advances in the development of novel biomaterials for delivery of RNA-based therapeutics and highlight their applications to treat GARDs.
Keywords: CRISPR; Genetic and rare diseases (GARDs); RNA delivery biomaterials; RNA therapeutics; RNAi; mRNA.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene Therapy with CRISPR/Cas9 Coming to Age for HIV Cure.AIDS Rev. 2017 Oct-Dec;19(3):167-172. AIDS Rev. 2017. PMID: 29019352
-
A New Era for Rare Genetic Diseases: Messenger RNA Therapy.Hum Gene Ther. 2019 Oct;30(10):1180-1189. doi: 10.1089/hum.2019.090. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Hum Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 31179759 Review.
-
mRNA therapies: Pioneering a new era in rare genetic disease treatment.J Control Release. 2024 May;369:696-721. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.03.056. Epub 2024 Apr 13. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 38580137 Review.
-
Next-generation therapeutics for rare genetic disorders.Mutagenesis. 2024 Apr 24;39(3):157-171. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geae002. Mutagenesis. 2024. PMID: 38332115 Review.
-
Why rare genetic diseases are a logical focus for RNA therapies.Nature. 2019 Oct;574(7778):S16-S18. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-03075-5. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31619800 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Efficient CRISPR-Cas9-based genome editing of β-globin gene on erythroid cells from homozygous β039-thalassemia patients.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021 Apr 3;21:507-523. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.03.025. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021. PMID: 33997100 Free PMC article.
-
Development of mRNA Lipid Nanoparticles: Targeting and Therapeutic Aspects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 22;25(18):10166. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810166. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lantern-shaped flexible RNA origami for Smad4 mRNA delivery and growth suppression of colorectal cancer.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 10;14(1):1307. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37020-y. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36894556 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA-based therapy proves superior to the standard of care for treating hereditary tyrosinemia 1 in a mouse model.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2022 Jul 15;26:294-308. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.07.006. eCollection 2022 Sep 8. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2022. PMID: 35949297 Free PMC article.
-
Applications and challenges of biomaterial mediated mRNA delivery.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3(4):428-444. doi: 10.37349/etat.2022.00093. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022. PMID: 36071982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

