Polyphenol-Based Particles for Theranostics
- PMID: 31244948
- PMCID: PMC6567970
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.31847
Polyphenol-Based Particles for Theranostics
Abstract
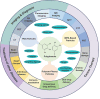
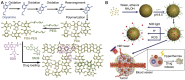
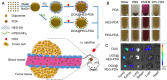
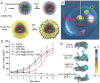
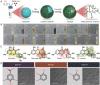
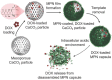
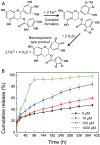
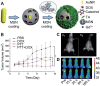
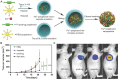
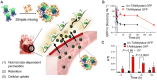
Polyphenols, due to their high biocompatibility and wide occurrence in nature, have attracted increasing attention in the engineering of functional materials ranging from films, particles, to bulk hydrogels. Colloidal particles, such as nanogels, hollow capsules, mesoporous particles and core-shell structures, have been fabricated from polyphenols or their derivatives with a series of polymeric or biomolecular compounds through various covalent and non-covalent interactions. These particles can be designed with specific properties or functionalities, including multi-responsiveness, radical scavenging capabilities, and targeting abilities. Moreover, a range of cargos (e.g., imaging agents, anticancer drugs, therapeutic peptides or proteins, and nucleic acid fragments) can be incorporated into these particles. These cargo-loaded carriers have shown their advantages in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, especially of cancer. In this review, we summarize the assembly of polyphenol-based particles, including polydopamine (PDA) particles, metal-phenolic network (MPN)-based particles, and polymer-phenol particles, and their potential biomedical applications in various diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: diagnosis; drug delivery; metal-phenolic networks; polydopamine particles; self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bioengineering of Metal-organic Frameworks for Nanomedicine.Theranostics. 2019 May 18;9(11):3122-3133. doi: 10.7150/thno.31918. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31244945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments of Supramolecular Metal-based Structures for Applications in Cancer Therapy and Imaging.Theranostics. 2019 May 18;9(11):3150-3169. doi: 10.7150/thno.31828. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31244947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticle-Based Biomineralization: A New Strategy toward Cancer Treatment.Theranostics. 2019 May 18;9(11):3134-3149. doi: 10.7150/thno.33539. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31244946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Janus particles: recent advances in the biomedical applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Aug 23;14:6749-6777. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S169030. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31692550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenol-Containing Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, and Therapeutic Delivery.Adv Mater. 2021 Jun;33(22):e2007356. doi: 10.1002/adma.202007356. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 33876449 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles modified by polydopamine: Working as "drug" carriers.Bioact Mater. 2020 Apr 18;5(3):522-541. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.04.003. eCollection 2020 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 32322763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenolic-enabled nanotechnology: versatile particle engineering for biomedicine.Chem Soc Rev. 2021 Apr 7;50(7):4432-4483. doi: 10.1039/d0cs00908c. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Chem Soc Rev. 2021. PMID: 33595004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ellagic acid-enhanced biocompatibility and bioactivity in multilayer core-shell gold nanoparticles for ameliorating myocardial infarction injury.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Sep 11;22(1):554. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02796-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39261890 Free PMC article.
-
All-in-one approaches for triple-negative breast cancer therapy: metal-phenolic nanoplatform for MR imaging-guided combinational therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 May 12;20(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01416-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35549947 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Systemic Toxicity, Genotoxicity, and Early Phase Hepatocarcinogenicity of Iron (III)-Tannic Acid Nanoparticles in Rats.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Mar 22;12(7):1040. doi: 10.3390/nano12071040. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quideau S, Deffieux D, Douat-Casassus C, Pouységu L. Plant polyphenols: Chemical properties, biological activities, and synthesis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011;50:586–621. - PubMed
-
- Haslam E, Cai Y. Plant polyphenols (vegetable tannins): Gallic acid metabolism. Nat Prod Rep. 1994;11:41–66. - PubMed
-
- Wigglesworth VB. The source of lipids and polyphenols for the insect cuticle: The role of fat-body, enocytes and enocytoids. Tissue Cell. 1988;20:919–32. - PubMed
-
- Krishnan G. Phenolic tanning and pigmentation of the cuticle in Carcinus maenas. Q J Microsc Sci. 1951;92:333–42.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

