Co-expression Network Analysis Elucidated a Core Module in Association With Prognosis of Non-functioning Non-invasive Human Pituitary Adenoma
- PMID: 31244774
- PMCID: PMC6563679
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00361
Co-expression Network Analysis Elucidated a Core Module in Association With Prognosis of Non-functioning Non-invasive Human Pituitary Adenoma
Abstract
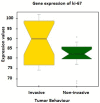
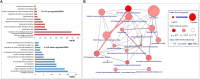
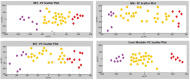
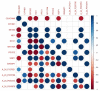
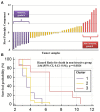
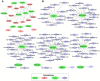
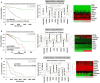
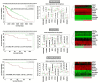
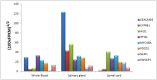
Non-functioning pituitary adenomas (NFPAs) are tumors with clinically challenging features since they have insidious progression. A complex network of gene interactions is thought to have roles in tumor formation and progression. Therefore, revealing the genetic network behind NFPA tumorigenesis is not only essential to attain further knowledge of tumor biology, but also plays a fundamental role in the development of efficacious treatment strategies. Differential co-expression network analysis is an outstanding approach for elucidation of groups of genes which show distinct co-expression patterns among phenotypes. In this study, we carried out a differential co-expression network analysis of NFPA-associated transcriptome dataset (n = 40) considering invasive (n = 22) and non-invasive (n = 18) phenotypes. Furthermore, we identified differentially co-expressed and co-regulated mRNA modules, which might be considered as potential systems biomarkers for NFPA prognosis and invasiveness. As a result, we have identified a novel 13-gene module, including CEACAM6, CYP4B1, EIF2S2, HID1, IFFO1, MYO18A, PDCD2, SGIP1, SWSAP1, and four unknown genes (A_24_P127621, A_24_P255786, A_24_P683553, and A_24_P916979), which was able to categorize the patients into two groups as invasive and non-invasive NFPA with distinct prognosis. The prognostic core module genes were associated with progression and prognosis of brain and glandular based cancers as well. Furthermore, these module genes were also expressed in blood, salivary gland, and spinal cord tissues. These results may provide the evidence on featured gene module which might play a prominent role in NFPA prognosis and sub-typing as effective biomarkers and therapeutic targets in the future.
Keywords: biomarker; co-expression; differential co-expression network; invasiveness; non-functional pituitary adenoma; prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying critical protein-coding genes and long non-coding RNAs in non-functioning pituitary adenoma recurrence.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):264. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12525. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33664827 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics-Based Signaling Pathway Network Alterations in Human Non-functional Pituitary Adenomas.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Dec 17;10:835. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00835. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31920959 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Important Invasion-Related Genes in Non-functional Pituitary Adenomas.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Aug;68(4):565-589. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01318-8. Epub 2019 Apr 13. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30982163
-
Recurrent non-functioning pituitary adenomas: a review on the new pathological classification, management guidelines and treatment options.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Oct;20(10):1233-1245. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1868-6. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29623588 Review.
-
Refractory nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas.Pituitary. 2023 Jun;26(3):278-280. doi: 10.1007/s11102-023-01298-4. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Pituitary. 2023. PMID: 36786972 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenomic and transcriptomic landscaping unraveled candidate repositioned therapeutics for non-functioning pituitary neuroendocrine tumors.J Endocrinol Invest. 2023 Apr;46(4):727-747. doi: 10.1007/s40618-022-01923-2. Epub 2022 Oct 28. J Endocrinol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36306107
-
Systematic Identification of Hub Genes in Placenta Accreta Spectrum Based on Integrated Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis.Front Genet. 2020 Sep 15;11:551495. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.551495. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33101378 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of the immune target CEACAM6 in cancer: a meta-analysis.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022 Jan 19;14:17588359211072621. doi: 10.1177/17588359211072621. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35082925 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis identifies a tumor subtype mRNA classifier for invasive non-functioning pituitary neuroendocrine tumor diagnostics.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(1):132-146. doi: 10.7150/thno.47525. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391466 Free PMC article.
-
A Transcriptome Community-and-Module Approach of the Human Mesoconnectome.Entropy (Basel). 2021 Aug 11;23(8):1031. doi: 10.3390/e23081031. Entropy (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Llyod RV, Osamura RY, Klöppel G, Rosai J. (eds.). WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; (2017). p. 355.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

