Metformin Modulates Cyclin D1 and P53 Expression to Inhibit Cell Proliferation and to Induce Apoptosis in Cervical Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 31244286
- PMCID: PMC7021606
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.6.1667
Metformin Modulates Cyclin D1 and P53 Expression to Inhibit Cell Proliferation and to Induce Apoptosis in Cervical Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
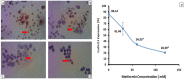
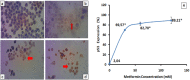
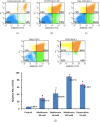
Background: Cervical cancer is one of the most prevalent gynecological cancers worldwide and contributes in high mortality of Indonesian women. The efficacy of chemotherapy as a standart therapy for cervical cancer decreases because it frequenly rises adverse effects. Recent studies have found that metformin has a potential anticancer effect mostly through reduction of cyclin expression and activation of Activated Adenosine Monophosphate Kinase (AMPK). This study aimed to investigate the effect of metfomin on expression of cyclin D1 and p53 and apoptosis in HeLa cancer cell line. Methods: HeLa cells were treated with various doses of metformin and doxorubicin as a positive control. Cytotoxic effect of metformin was determined using the MTT assay. Immunocytochemistry was used to assess cyclin D1 and p53 expression and apoptosis levels of treated HeLa cells were analyzed using flowcytometry. Data of cyclin D1 expression was statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Tamhane test, whilst ANOVA and Tukey post Hoc tests were used to analyze data of p53 and apoptosis level. The significant value was p< 0.05. Results: Metformin was able to inhibit proliferation of HeLa cells with IC50 60 mM. HeLa cells treated with 60 and 120 mM metformin had lower cyclin D1 expression than HeLa cells treated without metformin and reached a significant difference (p= 0.001). Moreover, 30 mM or higher doses of metformin increase significantly p53 expression (p< 0.001). Induction of apoptosis was observed in HeLa cells treated with all doses of metformin and reached statistically difference (p= 0.04 and p < 0.001). Conclusion: Metformin can modulate cyclin D1 and p53 expression in HeLa cancer cell line, leading to inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Other cyclin family members, CDK inhibitors and AMPK signaling should be further investigated in order to know mechanism of metformin action.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cyclin D1; HeLa cell; Metformin; p53.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metformin promotes apoptosis in primary breast cancer cells by downregulation of cyclin D1 and upregulation of P53 through an AMPK-alpha independent mechanism.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Apr 30;51(2):826-834. doi: 10.3906/sag-1908-112. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33350292 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin induces apoptosis and inhibits migration by activating the AMPK/p53 axis and suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling in human cervical cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):88. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11725. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33236135 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin induces degradation of cyclin D1 via AMPK/GSK3β axis in ovarian cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Feb;56(2):349-358. doi: 10.1002/mc.22498. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 27128966
-
Metformin as a Potential In Vitro Anticancer Modulator of Adenosine Monophosphate Kinase: A Review.Int J Breast Cancer. 2024 Aug 27;2024:1094274. doi: 10.1155/2024/1094274. eCollection 2024. Int J Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39246697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of cancer cell killing by metformin: a review on different cell death pathways.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Jan;478(1):197-214. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04502-4. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 35771397 Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin induces caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis in human bladder cancer T24 cells.Anticancer Drugs. 2020 Aug;31(7):655-662. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000966. Anticancer Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32568826 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of Mitochondrial Dynamics Mediated by Dynamin-Related Protein 1 in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 30;10:913904. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.913904. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35846374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin and Malignant Tumors: Not Over the Hill.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Aug 17;14:3673-3689. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S326378. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34429626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs as potential targets in metformin therapy for cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03516-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39354464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factorIRX5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by regulating the p53 signalling pathway.Cell Biochem Funct. 2020 Jul;38(5):621-629. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3517. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020. PMID: 32153043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, et al. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:909–15. - PubMed
-
- Amundson SA, Myers TG, Fornace AJ. Roles for p53 in growth arrest and apoptosis: Putting on the brakes after genotoxic stress. Oncogene. 1998;17:3287–99. - PubMed
-
- Aziz MF. Masalah pada kanker serviks. Cermin Dunia Kedokteran. 2001;133:5–7.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

