The Aspergillus fumigatus Mucin MsbA Regulates the Cell Wall Integrity Pathway and Controls Recognition of the Fungus by the Immune System
- PMID: 31217305
- PMCID: PMC6584374
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00350-19
The Aspergillus fumigatus Mucin MsbA Regulates the Cell Wall Integrity Pathway and Controls Recognition of the Fungus by the Immune System
Abstract
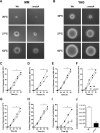
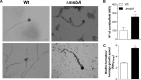
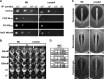
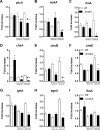
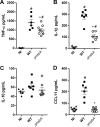
Aspergillus fumigatus is a filamentous fungus which causes invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised individuals. In fungi, cell signaling and cell wall plasticity are crucial for maintaining physiologic processes. In this context, Msb2 is an important signaling mucin responsible for activation of a variety of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent signaling pathways that regulate cell growth in several organisms, such as the cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway. Here, we aimed to characterize the MSB2 homologue in A. fumigatus Our results showed that MsbA plays a role in the vegetative and reproductive development of the fungus, in stress adaptation, and in resistance to antifungal drugs by modulating the CWI pathway gene expression. Importantly, cell wall composition is also responsible for activation of diverse receptors of the host immune system, thus leading to a proper immune response. In a model of acute Aspergillus pulmonary infection, results demonstrate that the ΔmsbA mutant strain induced less inflammation with diminished cell influx into the lungs and lower cytokine production, culminating in increased lethality rate. These results characterize for the first time the role of the signaling mucin MsbA in the pathogen A. fumigatus, as a core sensor for cell wall morphogenesis and an important regulator of virulence.IMPORTANCEAspergillus fumigatus is an opportunistic fungus with great medical importance. During infection, Aspergillus grows, forming hyphae that colonize the lung tissue and invade and spread over the mammal host, resulting in high mortality rates. The knowledge of the mechanisms responsible for regulation of fungal growth and virulence comprises an important point to better understand fungal physiology and host-pathogen interactions. Msb2 is a mucin that acts as a sensor and an upstream regulator of the MAPK pathway responsible for fungal development in Candida albicans and Aspergillus nidulans Here, we show the role of the signaling mucin MsbA in the pathogen A. fumigatus, as a core sensor for cell wall morphogenesis, fungal growth, and virulence. Moreover, we show that cell wall composition, controlled by MsbA, is detrimental for fungal recognition and clearance by immune cells. Our findings are important for the understanding of how fungal sensors modulate cell physiology.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; cell wall integrity; immune response; msb2; mucin; virulence.
Copyright © 2019 Gurgel et al.
Figures


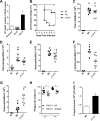
Similar articles
-
Putative Membrane Receptors Contribute to Activation and Efficient Signaling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades during Adaptation of Aspergillus fumigatus to Different Stressors and Carbon Sources.mSphere. 2020 Sep 16;5(5):e00818-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00818-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32938702 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus G-Protein Coupled Receptors GprM and GprJ Are Important for the Regulation of the Cell Wall Integrity Pathway, Secondary Metabolite Production, and Virulence.mBio. 2020 Oct 13;11(5):e02458-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02458-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33051372 Free PMC article.
-
The Aspergillus fumigatus Phosphoproteome Reveals Roles of High-Osmolarity Glycerol Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Promoting Cell Wall Damage and Caspofungin Tolerance.mBio. 2020 Feb 4;11(1):e02962-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02962-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32019798 Free PMC article.
-
Genes and molecules involved in Aspergillus fumigatus virulence.Rev Iberoam Micol. 2005 Mar;22(1):1-23. doi: 10.1016/s1130-1406(05)70001-2. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2005. PMID: 15813678 Review.
-
Cell wall antigens in Aspergillus fumigatus.Arch Med Res. 1993 Autumn;24(3):269-74. Arch Med Res. 1993. PMID: 8298277 Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved signaling modules regulate filamentous growth in fungi: a model for eukaryotic cell differentiation.Genetics. 2024 Oct 7;228(2):iyae122. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae122. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 39239926 Review.
-
The membrane mucin Msb2 regulates aflatoxin biosynthesis and pathogenicity in fungus Aspergillus flavus.Microb Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;14(2):628-642. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13701. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Microb Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33159717 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Wall Integrity and Its Industrial Applications in Filamentous Fungi.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Apr 23;8(5):435. doi: 10.3390/jof8050435. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35628691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and expression of fungal defensin in Escherichia coli and its antifungal mechanism by RNA-seq analysis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 14;14:1172257. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1172257. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37389349 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Treatment Approach for Aspergilloses by Targeting Germination.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jul 22;8(8):758. doi: 10.3390/jof8080758. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rocha MC, Godoy KF, de Castro PA, Hori JI, Bom VLP, Brown NA, Cunha AF, Goldman GH, Malavazi I. 2015. The Aspergillus fumigatus pkcA G579R mutant is defective in the activation of the cell wall integrity pathway but is dispensable for virulence in a neutropenic mouse infection model. PLoS One 10:e0135195. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135195. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rocha MC, Fabri J, de Godoy KF, de Castro PA, Hori JI, da Cunha AF, Arentshorst M, Ram AFJ, van den Hondel C, Goldman GH, Malavazi I. 2016. Aspergillus fumigatus MADS-box transcription factor rlmA is required for regulation of the cell wall integrity and virulence. G3 (Bethesda) 6:2983–3002. doi:10.1534/g3.116.031112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

