Development of a novel ssDNA aptamer targeting neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and its application in clinical trials
- PMID: 31215436
- PMCID: PMC6582607
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-1955-7
Development of a novel ssDNA aptamer targeting neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and its application in clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a promising biomarker of early diagnosis and prediction for acute kidney injury (AKI). However, the current program for NGAL detection is not extensively applied in clinics due to the high expense of antibodies. Nucleic acid aptamers are single-strand DNAs or RNAs which could bind to targets with high specificity and affinity, and they have been widely used in the diagnosis and therapy for multiple diseases. It is valuable for us to develop a new method for NGAL detection using aptamers instead of antibodies to achieve increased efficiency and decreased cost.
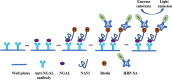
Methods: Nucleic acid aptamers against NGAL were obtained after SELEX process using magnetic beads, and an enzyme-linked aptamer analysis (ELAA), which can be widely used in clinical diagnosis at low cost, were successfully established. The feasibility of ELAA was further validated with urine samples harvested from 43 AKI patients and 30 healthy people.
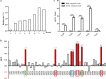
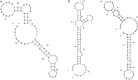
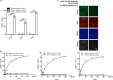
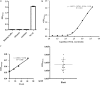
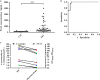
Results: Three candidate aptamers, including NA36, NA42 and NA53, were obtained after 8 rounds of SELEX process with magnetic beads and verified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), and the Kd value of each aptamer was 43.59, 66.55 and 32.52 nM, respectively. Moreover, the linear relationship was consistent at the range of 125-4000 ng/mL, and the detection limit of ELAA assay was 30.45 ng/mL. We also found that NGAL could be exclusively detected with NA53, and no cross-reaction between NA53 and human albumin or globulin occurred, the coefficient of variation (CV) between inner-plate and inter-plate was less than 15%, and the recovery rate was between 80 and 110%. Moreover, the sensitivity and specificity of ELAA assay in this study are 100% and 90%, respectively. Consistently, these results could also diagnose whether the occurrence of AKI in lots of patients, which has been demonstrated with the ELAA method we established after using NA53.
Conclusions: Taken together, NA53, the best candidate aptamer targeting NGAL protein, can be applied in clinical testing.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Aptamers; NGAL protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinalysis is more specific and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is more sensitive for early detection of acute kidney injury.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 May;28(5):1175-85. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs127. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 22529161 Clinical Trial.
-
Optimal cut points of plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for the prediction of acute kidney injury among critically ill adults: retrospective determination and clinical validation of a prospective multicentre study.BMJ Open. 2017 Jul 10;7(7):e016028. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016028. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28698338 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and Identification of ssDNA Aptamers against HN Protein for Detection of Bovine Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Antibodies in Serum.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2018;19(11):896-901. doi: 10.2174/1389201019666181031154046. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30381069
-
Is plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin a predictive biomarker for acute kidney injury in sepsis patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Crit Care. 2016 Jun;33:213-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.02.014. Epub 2016 Feb 26. J Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27017333 Review.
-
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker of Allograft Function After Renal Transplantation: Evaluation of the Current Status and Future Insights.Artif Organs. 2018 Jan;42(1):8-14. doi: 10.1111/aor.13039. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Artif Organs. 2018. PMID: 29266311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleic Acid Nanotechnology for Diagnostics and Therapeutics in Acute Kidney Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 13;23(6):3093. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063093. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning guided aptamer refinement and discovery.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 22;12(1):2366. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22555-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33888692 Free PMC article.
-
Structurally Different Yet Functionally Similar: Aptamers Specific for the Ebola Virus Soluble Glycoprotein and GP1,2 and Their Application in Electrochemical Sensing.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 27;24(5):4627. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054627. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902059 Free PMC article.
-
SERS based Y-shaped aptasensor for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury.RSC Adv. 2022 May 26;12(25):15910-15917. doi: 10.1039/d2ra02813a. eCollection 2022 May 23. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35733690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Candido S, Abrams SL, Steelman LS, Lertpiriyapong K, Fitzgerald TL, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Montalto G, Cervello M, Polesel J, et al. Roles of NGAL and MMP-9 in the tumor microenvironment and sensitivity to targeted therapy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Res. 2016;1863:438–448. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.08.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bellmann-Weiler R, Schroll A, Engl S, Nairz M, Talasz H, Seifert M, Weiss G. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and interleukin-10 regulate intramacrophage Chlamydia pneumoniae replication by modulating intracellular iron homeostasis. Immunobiology. 2013;218:969–978. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.11.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

