Hippocampal BDNF regulates a shift from flexible, goal-directed to habit memory system function following cocaine abstinence
- PMID: 31206907
- PMCID: PMC6851590
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.23127
Hippocampal BDNF regulates a shift from flexible, goal-directed to habit memory system function following cocaine abstinence
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Hippocampal BDNF regulates a shift from flexible, goal-directed to habit memory system function following cocaine abstinence.Hippocampus. 2020 Dec;30(12):1327. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23277. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Hippocampus. 2020. PMID: 33241886 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
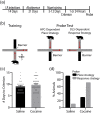
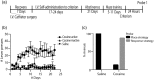
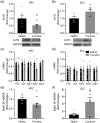
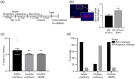
The transition from recreational drug use to addiction involves pathological learning processes that support a persistent shift from flexible, goal-directed to habit behavioral control. Here, we examined the molecular mechanisms supporting altered function in hippocampal (HPC) and dorsolateral striatum (DLS) memory systems following abstinence from repeated cocaine. After 3 weeks of cocaine abstinence (experimenter- or self-administered), we tested new behavioral learning in male rats using a dual-solution maze task, which provides an unbiased approach to assess HPC- versus DLS-dependent learning strategies. Dorsal hippocampus (dHPC) and DLS brain tissues were collected after memory testing to identify transcriptional adaptations associated with cocaine-induced shifts in behavioral learning. Our results demonstrate that following prolonged cocaine abstinence rats show a bias toward the use of an inflexible, habit memory system (DLS) in lieu of a more flexible, easily updated memory system involving the HPC. This memory system bias was associated with upregulation and downregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene expression and transcriptionally permissive histone acetylation (acetylated histone H3, AcH3) in the DLS and dHPC, respectively. Using viral-mediated gene transfer, we overexpressed BDNF in the dHPC during cocaine abstinence and new maze learning. This manipulation restored HPC-dependent behavioral control. These findings provide a system-level understanding of altered plasticity and behavioral learning following cocaine abstinence and inform mechanisms mediating the organization of learning and memory more broadly.
Keywords: BDNF; dorsolateral striatum; gene transcription; hippocampus; learning and memory; psychostimulants.
© 2019 The Authors. Hippocampus published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in the ventral tegmental area during cocaine abstinence is associated with increased histone acetylation at BDNF exon I-containing promoters.J Neurochem. 2012 Jan;120(2):202-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07571.x. Epub 2011 Nov 28. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22043863 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal memory system function and the regulation of cocaine self-administration behavior in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2004 May 5;151(1-2):225-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2003.08.020. Behav Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15084439
-
Dopamine in the dorsal hippocampus impairs the late consolidation of cocaine-associated memory.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Jun;39(7):1645-53. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.11. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24442095 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosterone effects on BDNF expression in the hippocampus. Implications for memory formation.Stress. 2000 May;3(3):201-8. doi: 10.3109/10253890009001124. Stress. 2000. PMID: 10938581 Review.
-
Use it and boost it with physical and mental activity.Hippocampus. 2013 Nov;23(11):1125-35. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22197. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23996382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of CSF1R, a receptor involved in microglia viability, alters behavioral and molecular changes induced by cocaine.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 6;11(1):15989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95059-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34362959 Free PMC article.
-
Neural substrates of habit.J Neurosci Res. 2020 Jun;98(6):986-997. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24552. Epub 2019 Nov 6. J Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 31693205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampus-sensitive and striatum-sensitive learning one month after morphine or cocaine exposure in male rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 Jun;217:173392. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173392. Epub 2022 May 2. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 35513118 Free PMC article.
-
Melamine disrupts spatial reversal learning and learning strategy via inhibiting hippocampal BDNF-mediated neural activity.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 11;16(1):e0245326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245326. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33428671 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

