Differential expression of EphA5 protein in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance
- PMID: 31186729
- PMCID: PMC6507474
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10167
Differential expression of EphA5 protein in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to evaluate ephrin type-A receptor 5 (EphA5) expression and its clinicopathological significance in gastric cancer. Gastric cancer tissues were analyzed by immunohistochemistry. The association between EphA5 expression and clinicopathological parameters, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status and Ki-67 proliferation index was statistically analyzed. EphA5 expression was detected in all non-tumor gastric epithelia but was differentially expressed among gastric cancer samples. EphA5 was negatively expressed in 30/110 (27.3%) and positively expressed in 80/110 (72.3%) samples from patients with gastric cancer. EphA5 expression was significantly associated with Lauren classification (P=0.032), lymph node metastasis (P<0.001), HER2 expression (P=0.020) and Ki-67 expression (P=0.005). No significant association was determined between EphA5 expression and age, sex, primary location, depth of invasion and Tumor-Node-Metastasis stage. The present data indicated that EphA5 is differentially expressed in gastric cancer. EphA5 may therefore be a potential therapeutic target and may have clinical utility as a marker for lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer.
Keywords: Ki-67; ephrin type-A receptor 5; gastric cancer; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2.
Figures
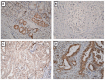
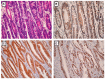
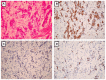
Similar articles
-
Reduced expression of EphA5 is associated with lymph node metastasis, advanced TNM stage, and poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma.Histol Histopathol. 2017 May;32(5):491-497. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-815. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Histol Histopathol. 2017. PMID: 27651378
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C and chemokine receptor CCR7 in gastric carcinoma and their values in predicting lymph node metastasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Mar 15;10(6):783-90. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.783. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15040017 Free PMC article.
-
The clinicopathological parameters and prognostic significance of HER2 expression in gastric cancer patients: a meta-analysis of literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 Mar 21;15(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1132-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28327158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased expression of EphA5 is associated with Fuhrman nuclear grade and pathological tumour stage in ccRCC.Int J Exp Pathol. 2017 Feb;98(1):34-39. doi: 10.1111/iep.12219. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Int J Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28421649 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA5 by promoter methylation in human breast cancer.Hum Pathol. 2010 Jan;41(1):48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.06.007. Epub 2009 Sep 5. Hum Pathol. 2010. PMID: 19733895
Cited by
-
Analysis of a Four-Component Competing Endogenous RNA Network Reveals Potential Biomarkers in Gastric Cancer: An Integrated Systems Biology and Experimental Investigation.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Oct 28;12:238. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_185_23. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 38073751 Free PMC article.
-
EphA5 Silencing Increases the Radiosensitivity of ESCC Cells Through ATM-Dependent Pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Oct 2;12:9539-9549. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S261182. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33061640 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple paragangliomas: a case report.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Sep 18;13(Suppl 8):125. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-00789-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32948182 Free PMC article.
-
EphA5 knockdown enhances the invasion and migration ability of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jan 13;20:20. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1101-x. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 31956298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:687–697. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61121-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szöllösi J, Balázs M, Feuerstein BG, Benz CC, Waldman FM. ERBB-2 (HER2/neu) gene copy number, p185HER-2 overexpression, and intratumor heterogeneity in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:5400–5407. - PubMed
-
- Ramieri MT, Murari R, Botti C, Pica E, Zotti G, Alo PL. Detection of HER2 amplification using the SISH technique in breast, colon, prostate, lung and ovarian carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:1287–1292. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
