A microRNA‑24‑to‑secretagogin regulatory pathway mediates cholesterol‑induced inhibition of insulin secretion
- PMID: 31173188
- PMCID: PMC6605698
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4224
A microRNA‑24‑to‑secretagogin regulatory pathway mediates cholesterol‑induced inhibition of insulin secretion
Abstract
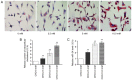
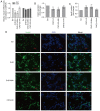
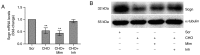
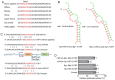
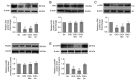
Hypercholesterolemia is a key factor leading to β‑cell dysfunction, but its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Secretagogin (Scgn), a Ca2+ sensor protein that is expressed at high levels in the islets, has been shown to play a key role in regulating insulin secretion through effects on the soluble N‑ethylmaleimide‑sensitive factor attachment receptor protein complexes. However, further studies are required to determine whether Scgn plays a role in hypercholesterolemia‑associated β‑cell dysfunction. The present study investigated the involvement of a microRNA‑24 (miR‑24)‑to‑Scgn regulatory pathway in cholesterol‑induced β‑cell dysfunction. In the present study, MIN6 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of cholesterol and then, the cellular functions and changes in the miR‑24‑to‑Scgn signal pathway were observed. Excessive uptake of cholesterol in MIN6 cells increased the expression of miR‑24, resulting in a reduction in Sp1 expression by directly targeting its 3' untranslated region. As a transcriptional activator of Scgn, downregulation of Sp1 decreased Scgn levels and subsequently decreased the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase and paxillin, which is regulated by Scgn. Therefore, the focal adhesions in insulin granules were impaired and insulin exocytosis was reduced. The present study concluded that a miR‑24‑to‑Scgn pathway participates in the mechanism regulating cholesterol accumulation‑induced β‑cell dysfunction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Secretagogin affects insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells by regulating actin dynamics and focal adhesion.Biochem J. 2016 Jun 15;473(12):1791-803. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160137. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27095850 Free PMC article.
-
A novel secretagogin/ATF4 pathway is involved in oxidized LDL-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and islet β-cell apoptosis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Jan 12;53(1):54-62. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa142. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33289795
-
Extracellular secretagogin is internalized into the cells through endocytosis.FEBS J. 2022 Jun;289(11):3183-3204. doi: 10.1111/febs.16338. Epub 2022 Jan 9. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34967502
-
Veiled Potential of Secretagogin in Diabetes: Correlation or Coincidence?Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Apr;30(4):234-243. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30772140 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in islet hormone secretion.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Sep;20 Suppl 2:11-19. doi: 10.1111/dom.13382. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 30230181 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Sequences Modulated by Beta Cell Lipid Metabolism: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Biology (Basel). 2021 Jun 15;10(6):534. doi: 10.3390/biology10060534. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The downregulation of SCGN induced by lipotoxicity promotes NLRP3-mediated β-cell pyroptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jul 27;10(1):340. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02107-y. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39068218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kruit JK, Kremer PH, Dai L, Tang R, Ruddle P, de Haan W, Brunham LR, Verchere CB, Hayden MR. Cholesterol efflux via ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and cholesterol uptake via the LDL receptor influences cholesterol-induced impairment of beta cell function in mice. Diabetologia. 2010;53:1110–1119. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1691-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

