Regulation of AMPK activity by type 10 adenylyl cyclase: contribution to the mitochondrial biology, cellular redox and energy homeostasis
- PMID: 31172217
- PMCID: PMC11105217
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03152-y
Regulation of AMPK activity by type 10 adenylyl cyclase: contribution to the mitochondrial biology, cellular redox and energy homeostasis
Abstract
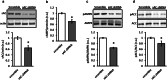
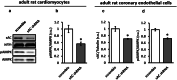
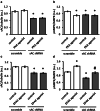
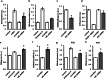
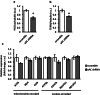
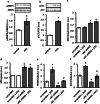
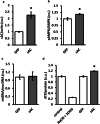
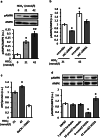
The downregulation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity contributes to numerous pathologies. Recent reports suggest that the elevation of cellular cAMP promotes AMPK activity. However, the source of the cAMP pool that controls AMPK activity remains unknown. Mammalian cells possess two cAMP sources: membrane-bound adenylyl cyclase (tmAC) and intracellularly localized, type 10 soluble adenylyl cyclase (sAC). Due to the localization of sAC and AMPK in similar intracellular compartments, we hypothesized that sAC may control AMPK activity. In this study, sAC expression and activity were manipulated in H9C2 cells, adult rat cardiomyocytes or endothelial cells. sAC knockdown depleted the cellular cAMP content and decreased AMPK activity in an EPAC-dependent manner. Functionally, sAC knockdown reduced cellular ATP content, increased mitochondrial ROS formation and led to mitochondrial depolarization. Furthermore, sAC downregulation led to EPAC-dependent mitophagy disturbance, indicated by an increased mitochondrial mass and unaffected mitochondrial biogenesis. Consistently, sAC overexpression or stimulation with bicarbonate significantly increased AMPK activity and cellular ATP content. In contrast, tmAC inhibition or stimulation produced no effect on AMPK activity. Therefore, the sAC-EPAC axis may regulate basal and induced AMPK activity and support mitophagy, cellular energy and redox homeostasis. The study argues for sAC as a potential target in treating pathologies associated with AMPK downregulation.
Keywords: ADCY10; AMPK; ATP; Mitophagy; ROS; cAMP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Mitochondrial Homeostasis by sAC-Derived cAMP Pool: Basic and Translational Aspects.Cells. 2021 Feb 22;10(2):473. doi: 10.3390/cells10020473. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33671810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble adenylyl cyclase regulates the cytosolic NADH/NAD+ redox state and the bioenergetic switch between glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2021 Apr 1;1862(4):148367. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2020.148367. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2021. PMID: 33412125
-
Protective role of soluble adenylyl cyclase against reperfusion-induced injury of cardiac cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Jan;1865(1):252-260. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.07.021. Epub 2018 Jul 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 30044950
-
Soluble adenylyl cyclase-mediated cAMP signaling and the putative role of PKA and EPAC in cerebral mitochondrial function.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Aug;97(8):1018-1038. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24477. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 31172581
-
Emerging Role of cAMP/AMPK Signaling.Cells. 2022 Jan 17;11(2):308. doi: 10.3390/cells11020308. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Mitochondrial Homeostasis by sAC-Derived cAMP Pool: Basic and Translational Aspects.Cells. 2021 Feb 22;10(2):473. doi: 10.3390/cells10020473. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33671810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Administration of Bicarbonate Protects Mitochondria, Rescues Retinal Ganglion Cells, and Ameliorates Visual Dysfunction Caused by Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 19;13(6):743. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060743. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929182 Free PMC article.
-
Bisdemethoxycurcumin alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via activating AMPKα pathway.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Nov 20;24(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00698-3. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37986186 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-Dependent Biphasic Action of Quetiapine on AMPK Signalling via 5-HT7 Receptor: Exploring Pathophysiology of Clinical and Adverse Effects of Quetiapine.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 14;23(16):9103. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169103. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012369 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the sAC-Dependent cAMP Pool to Prevent SARS-Cov-2 Infection.Cells. 2020 Aug 25;9(9):1962. doi: 10.3390/cells9091962. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32854430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yamauchi T., Kamon J., Minokoshi Y., Ito Y., Waki H., Uchida S., Yamashita S., Noda M., Kita S., Ueki K., Eto K., Akanuma Y., Froguel P., Foufelle F., Ferre P., Carling D., Kimura S., Nagai R., Kahn B.B., Kadowaki T. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature Medicine. 2002;8(11):1288–1295. doi: 10.1038/nm788. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

