TGF-β induces liver fibrosis via miRNA-181a-mediated down regulation of augmenter of liver regeneration in hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 31166951
- PMCID: PMC6550375
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214534
TGF-β induces liver fibrosis via miRNA-181a-mediated down regulation of augmenter of liver regeneration in hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
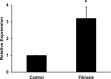
Objective: To study the role of miRNA-181a and augmenter of liver regeneration in TGF-β-induced fibrosis in hepatic stellate cells.
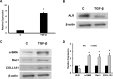
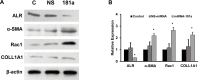
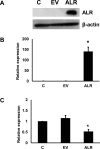
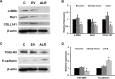
Methods: LX2 cells were treated with 20 ng/ml TGF-β for 24 h. miRNA-181a, ALR plasmid and empty vectors were transfected using siPORT NeoFx reagent. Cells were harvested after 48 h or 72 h of transfection for protein or RNA analysis. Western blotting was performed for ALR, TGF-β receptor II (TGFβ-RII), collagen 1A1 (COLL1A1), alpha-smooth muscle cell actin (α-SMA), rac1, E-cadherin and β-actin. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed for ALR, GAPDH, miRNA-181a or 5S rRNA.
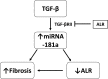
Results: TGF-β induced the expression of miRNA-181a, which in turn down-regulated ALR thereby induced the fibrosis markers, such as COLL1A1, α-SMA and rac1 in hepatic stellate cells. Over-expression of miRNA-181a down-regulated expression of ALR and up-regulated expression of fibrosis markers. On the other hand, ALR over-expression resulted in a decrease in miRNA-181a expression and fibrosis markers. Over-expression of ALR also inhibited the expression of TGFβ-RII and increased expression E-cadherin.
Conclusion: TGF-β induced miRNA-181a, which in turn induced fibrosis, at least in part, by inhibiting ALR. ALR inhibited TGF-β action by decreasing the expression of TGFβ-RII, thereby inhibiting miRNA-181a expression and fibrosis markers. ALR could serve as a potential molecule to inhibit liver fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deficiency in augmenter of liver regeneration accelerates liver fibrosis by promoting migration of hepatic stellate cell.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Nov;1864(11):3780-3791. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 30251695
-
Hes1, an important gene for activation of hepatic stellate cells, is regulated by Notch1 and TGF-β/BMP signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 21;21(3):878-87. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.878. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25624721 Free PMC article.
-
Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA) Reduces Fibrosis Markers and Deactivates Human Stellate Cells via the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT).Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Jun;79(2):349-357. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-00974-1. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33689126
-
Augmenter of liver regeneration: Mitochondrial function and steatohepatitis.J Hepatol. 2022 Nov;77(5):1410-1421. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.019. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35777586 Review.
-
The protective roles of augmenter of liver regeneration in hepatocytes in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 11;13:928606. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.928606. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36304168 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ability of a Combined FIB4/miRNA181a Score to Predict Significant Liver Fibrosis in NAFLD Patients.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 24;9(12):1751. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121751. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944567 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology and Treatment Options for Hepatic Fibrosis: Can It Be Completely Cured?Cells. 2021 May 4;10(5):1097. doi: 10.3390/cells10051097. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34064375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amniotic Membrane and Its Derivatives: Novel Therapeutic Modalities in Liver Disorders.Cells. 2023 Aug 21;12(16):2114. doi: 10.3390/cells12162114. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in the modulation of cancer-associated fibroblasts activity during pancreatic cancer pathogenesis.J Physiol Biochem. 2023 Feb;79(1):193-204. doi: 10.1007/s13105-022-00899-0. Epub 2022 Jun 29. J Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 35767180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs shared between activated human hepatic stellate cells and nash fibrosis.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Mar 24;22:100753. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100753. eCollection 2020 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 32258441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davoodian P, Ravanshad M, Hosseini SY, Khanizadeh S, Almasian M, Nejati Zadeh A, et al. Effect of TGF-beta/smad signaling pathway blocking on expression profiles of miR-335, miR-150, miR-194, miR-27a, and miR-199a of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2017;10(2):112–7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

