Low cardiac lipolysis reduces mitochondrial fission and prevents lipotoxic heart dysfunction in Perilipin 5 mutant mice
- PMID: 31166588
- PMCID: PMC7338219
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvz119
Low cardiac lipolysis reduces mitochondrial fission and prevents lipotoxic heart dysfunction in Perilipin 5 mutant mice
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Low cardiac lipolysis reduces mitochondrial fission and prevents lipotoxic heart dysfunction in Perilipin 5 mutant mice.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Nov 1;115(13):1906. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz189. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 31363747 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
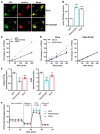
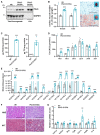
Aims: Lipotoxic cardiomyopathy in diabetic and obese patients typically encompasses increased cardiac fatty acid (FA) uptake eventually surpassing the mitochondrial oxidative capacity. Lowering FA utilization via inhibition of lipolysis represents a strategy to counteract the development of lipotoxic heart dysfunction. However, defective cardiac triacylglycerol (TAG) catabolism and FA oxidation in humans (and mice) carrying mutated ATGL alleles provokes lipotoxic heart dysfunction questioning a therapeutic approach to decrease cardiac lipolysis. Interestingly, decreased lipolysis via cardiac overexpression of Perilipin 5 (Plin5), a binding partner of ATGL, is compatible with normal heart function and lifespan despite massive cardiac lipid accumulation. Herein, we decipher mechanisms that protect Plin5 transgenic mice from the development of heart dysfunction.
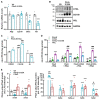
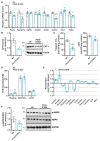
Methods and results: We generated mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of Plin5 encoding a serine-155 to alanine exchange (Plin5-S155A) of the protein kinase A phosphorylation site, which has been suggested as a prerequisite to stimulate lipolysis and may play a crucial role in the preservation of heart function. Plin5-S155A mice showed a substantial increase in cardiac TAG and ceramide levels, which was comparable to mice overexpressing non-mutated Plin5. Lipid accumulation was compatible with normal heart function even under mild stress. Plin5-S155A mice showed reduced cardiac FA oxidation but normal ATP production and changes in the Plin5-S155A phosphoproteome compared to Plin5 transgenic mice. Interestingly, mitochondrial recruitment of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) was markedly reduced in cardiac muscle of Plin5-S155A and Plin5 transgenic mice accompanied by decreased phosphorylation of mitochondrial fission factor, a mitochondrial receptor of Drp1.
Conclusions: This study suggests that low cardiac lipolysis is associated with reduced mitochondrial fission and may represent a strategy to combat the development of lipotoxic heart dysfunction.
Keywords: Cardiac lipolysis; Heart dysfunction; Lipotoxicity; Mitochondrial dynamics; Perilipin 5.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
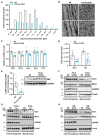
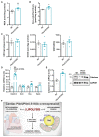
Similar articles
-
The interplay of protein kinase A and perilipin 5 regulates cardiac lipolysis.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 16;290(3):1295-306. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.604744. Epub 2014 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25418045 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin reduces lipid accumulation in the liver by activating protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of perilipin 5.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Dec;1862(12):1512-1519. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28919478
-
Cardiac-specific overexpression of perilipin 5 provokes severe cardiac steatosis via the formation of a lipolytic barrier.J Lipid Res. 2013 Apr;54(4):1092-102. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M034710. Epub 2013 Jan 23. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23345410 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin 5, a lipid droplet protein adapted to mitochondrial energy utilization.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014 Apr;25(2):110-7. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000057. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014. PMID: 24535284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of mitochondrial bioenergetics by the non-canonical roles of mitochondrial dynamics proteins in the heart.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 May;1864(5 Pt B):1991-2001. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 28918113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pivotal role of vitamin D in mitochondrial health, cardiac function, and human reproduction.EXCLI J. 2022 Jul 20;21:967-990. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-4935. eCollection 2022. EXCLI J. 2022. PMID: 36110560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid overload-induced RTN3 activation leads to cardiac dysfunction by promoting lipid droplet biogenesis.Cell Death Differ. 2024 Mar;31(3):292-308. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01241-x. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Cell Death Differ. 2024. PMID: 38017147 Free PMC article.
-
Pgam5 aggravates hyperglycemia-induced myocardial dysfunction through disrupting Phb2-dependent mitochondrial dynamics.Int J Med Sci. 2024 May 5;21(7):1194-1203. doi: 10.7150/ijms.92872. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38818468 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin 5 regulates hepatic stellate cell activation and high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Animal Model Exp Med. 2024 Apr;7(2):166-178. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12327. Epub 2023 May 18. Animal Model Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 37202925 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Mechanisms in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Diabetes Metab J. 2020 Feb;44(1):33-53. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0185. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. PMID: 32097997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schaffer JE. Lipotoxicity: when tissues overeat. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003;14:281–287. - PubMed
-
- Szczepaniak LS, Victor RG, Orci L, Unger RH. Forgotten but not gone: the rediscovery of fatty heart, the most common unrecognized disease in America. Circ Res. 2007;101:759–767. - PubMed
-
- Lopaschuk GD, Spafford MA, Davies NJ, Wall SR. Glucose and palmitate oxidation in isolated working rat hearts reperfused after a period of transient global ischemia. Circ Res. 1990;66:546–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

