Evaluation of the Salivary Level of Cortisol in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31137861
- PMCID: PMC6571959
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina55050213
Evaluation of the Salivary Level of Cortisol in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
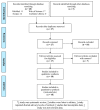
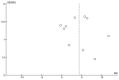
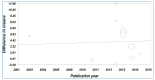
Background and objective: Cortisol, as the main human glucocorticoid, is considered to be a biological marker of stress and anxiety. Since it is known that oral lichen planus (OLP) can appear and worsen during stressful events, cortisol levels have been previously studied in OLP patients. The present meta-analysis aims to assess the salivary concentration of cortisol in OLP patients compared to healthy controls. Materials and methods: Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Scopus databases were searched up to October 2018. The RevMan 5.3 software was used with the mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The CMA 2.0 Software was used to evaluate the publication bias, sensitivity analysis, and meta-regression as possible sources of heterogeneity. Results: 10 studies were analyzed and a total of 269 OLP patients and 268 controls were included. The pooled MD of the salivary levels of cortisol in OLP patients compared with controls was 4.27 ng/mL (95% CI: 2.33, 6.21; P < 0.0001), thus, the salivary level of cortisol in OLP patients was significantly higher than in controls. In Indian-based population studies, a significant difference in the salivary cortisol levels in OLP patients compared with controls was detected (MD = 5.62 ng/mL; 95% CI: 2.67, 8.56; P = 0.0002). In addition, a significant difference in the salivary cortisol levels in the OLP patients compared with the controls was obtained in studies performed with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method (MD = 5.33 ng/mL; 95% CI: 2.72, 7.93; P < 0.0001). Conclusion: We suggest that supportive psychological treatment together with the conventional therapy could increase patients' capability to prevent stress, anxiety, and depression.
Keywords: cortisol; meta-analysis; oral lichen planus; saliva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Salivary biomarkers to evaluate psychological disorders in oral lichen planus: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Oral Dis. 2023 Oct;29(7):2734-2746. doi: 10.1111/odi.14385. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Oral Dis. 2023. PMID: 36161740
-
Evaluation of salivary cortisol and psychological factors in patients with oral lichen planus.Indian J Dent Res. 2009 Jul-Sep;20(3):288-92. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.57361. Indian J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 19884710
-
Cytokines, cortisol, and nitric oxide as salivary biomarkers in oral lichen planus: a systematic review.Braz Oral Res. 2018 Aug 13;32:e82. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2018.vol32.0082. Braz Oral Res. 2018. PMID: 30110084 Review.
-
The evaluation of anxiety and salivary cortisol levels in patients with oral lichen planus.Oral Dis. 2003 Nov;9(6):298-301. doi: 10.1034/j.1601-0825.2003.00960.x. Oral Dis. 2003. PMID: 14629330
-
Salivary and serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in oral lichen planus: a systematic review and meta-analysis study.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2017 Sep;124(3):e183-e189. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2017.06.117. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28823317 Review.
Cited by
-
Desquamative Gingivitis in the Context of Autoimmune Bullous Dermatoses and Lichen Planus-Challenges in the Diagnosis and Treatment.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jul 20;12(7):1754. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12071754. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Cortisol Levels in Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Indian J Dermatol. 2021 Nov-Dec;66(6):654-659. doi: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_95_21. Indian J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 35283522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary metabolomics in patients with oral lichen planus: a preliminary study based on NMR spectroscopy.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Jan 18;28(1):103. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05389-1. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38236502 Free PMC article.
-
Hypha essential genes in Candida albicans pathogenesis of oral lichen planus: an in-vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2021 Dec 1;21(1):614. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01975-5. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 34852796 Free PMC article.
-
A Study of Oral Health Parameters and the Properties and Composition of Saliva in Oncological Patients with and without Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Who Take Bisphosphonates.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jun 2;59(6):1073. doi: 10.3390/medicina59061073. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37374277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaur B., Sunil M.K., Trivedi A., Singla N., Garg S., Goyal N. Salivary Cortisol as a Diagnostic Marker in Oral Lichen Planus. J. Int. Oral Health. 2015;7:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffari H.R., Ramezani M., Mahmoudiahmadabadi M., Omidpanah N., Sadeghi M. Salivary and serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2017;124:e183–e189. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2017.06.117. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

