Preserving Genome Integrity During the Early Embryonic DNA Replication Cycles
- PMID: 31137726
- PMCID: PMC6563053
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10050398
Preserving Genome Integrity During the Early Embryonic DNA Replication Cycles
Abstract
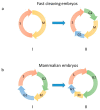
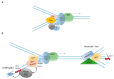
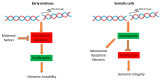
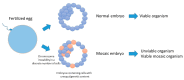
During the very early stages of embryonic development chromosome replication occurs under rather challenging conditions, including a very short cell cycle, absence of transcription, a relaxed DNA damage response and, in certain animal species, a highly contracted S-phase. This raises the puzzling question of how the genome can be faithfully replicated in such a peculiar metabolic context. Recent studies have provided new insights into this issue, and unveiled that embryos are prone to accumulate genetic and genomic alterations, most likely due to restricted cellular functions, in particular reduced DNA synthesis quality control. These findings may explain the low rate of successful development in mammals and the occurrence of diseases, such as abnormal developmental features and cancer. In this review, we will discuss recent findings in this field and put forward perspectives to further study this fascinating question.
Keywords: Caenorabditis elegans; DNA damage; DNA damage tolerance; Drosophila melanogaster; Xenopus laevis; iPSCs; mouse embryonic stem cells; replication stress; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome wide decrease of DNA replication eye density at the midblastula transition of Xenopus laevis.Cell Cycle. 2019 Jul;18(13):1458-1472. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1618641. Epub 2019 May 26. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31130065 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic genome instability upon DNA replication timing program emergence.Nature. 2024 Sep;633(8030):686-694. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07841-y. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39198647 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of RTF2 from Stalled Replisomes Promotes Maintenance of Genome Integrity.Mol Cell. 2018 Jan 4;69(1):24-35.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.11.035. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29290612 Free PMC article.
-
Replication Stress and Consequential Instability of the Genome and Epigenome.Molecules. 2019 Oct 27;24(21):3870. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213870. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31717862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ensuring the stability of the genome: DNA damage checkpoints.ScientificWorldJournal. 2001 Nov 20;1:684-702. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2001.297. ScientificWorldJournal. 2001. PMID: 12805771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cleavage of Early Mouse Embryo with Damaged DNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 23;23(7):3516. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073516. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408877 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Mechanisms Against DNA Replication Stress in the Nervous System.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jun 30;11(7):730. doi: 10.3390/genes11070730. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human embryonic genetic mosaicism and its effects on development and disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Oct;25(10):698-714. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00715-z. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 38605218 Review.
-
DNA repair genes play a variety of roles in the development of fish embryos.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 1;11:1119229. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1119229. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36936683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Heritability of Replication Problems.Cells. 2021 Jun 11;10(6):1464. doi: 10.3390/cells10061464. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34207969 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

