HspB1 phosphorylation regulates its intramolecular dynamics and mechanosensitive molecular chaperone interaction with filamin C
- PMID: 31131323
- PMCID: PMC6530996
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aav8421
HspB1 phosphorylation regulates its intramolecular dynamics and mechanosensitive molecular chaperone interaction with filamin C
Abstract
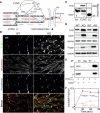
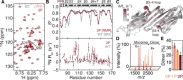
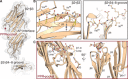
Mechanical force-induced conformational changes in proteins underpin a variety of physiological functions, typified in muscle contractile machinery. Mutations in the actin-binding protein filamin C (FLNC) are linked to musculoskeletal pathologies characterized by altered biomechanical properties and sometimes aggregates. HspB1, an abundant molecular chaperone, is prevalent in striated muscle where it is phosphorylated in response to cues including mechanical stress. We report the interaction and up-regulation of both proteins in three mouse models of biomechanical stress, with HspB1 being phosphorylated and FLNC being localized to load-bearing sites. We show how phosphorylation leads to increased exposure of the residues surrounding the HspB1 phosphosite, facilitating their binding to a compact multidomain region of FLNC proposed to have mechanosensing functions. Steered unfolding of FLNC reveals that its extension trajectory is modulated by the phosphorylated region of HspB1. This may represent a posttranslationally regulated chaperone-client protection mechanism targeting over-extension during mechanical stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutations in HspB1 and hereditary neuropathies.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020 Jul;25(4):655-665. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01099-9. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020. PMID: 32301006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of stress-induced intracellular sorting and chaperone function of Hsp27 (HspB1) in mammalian cells.Biochem J. 2007 Nov 1;407(3):407-17. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070195. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17650072 Free PMC article.
-
Small heat-shock proteins and their role in mechanical stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020 Jul;25(4):601-613. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01095-z. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020. PMID: 32253742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filamin C is a highly dynamic protein associated with fast repair of myofibrillar microdamage.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Jul 1;25(13):2776-2788. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw135. Epub 2016 May 19. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27206985
-
Role of Filamin C in Muscle Cells.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024 Sep;89(9):1546-1557. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924090025. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024. PMID: 39418514 Review.
Cited by
-
Under construction: The dynamic assembly, maintenance, and degradation of the cardiac sarcomere.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020 Nov;148:89-102. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.08.018. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32920010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights Into the Role of Heat Shock Protein 27 in the Development of Neurodegeneration.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Mar 30;15:868089. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.868089. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35431800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of the small heat shock protein HspB1 regulates cytoskeletal recruitment and cell motility.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Sep 15;33(11):ar100. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E22-02-0057. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35767320 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Function of Filamin C in the Muscle Z-Disc.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 13;21(8):2696. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082696. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32295012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural visualization of the tubulin folding pathway directed by human chaperonin TRiC/CCT.Cell. 2022 Dec 8;185(25):4770-4787.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.014. Cell. 2022. PMID: 36493755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tarone G., Brancaccio M., Keep your heart in shape: Molecular chaperone networks for treating heart disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 102, 346–361 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Willis M. S., Patterson C., Proteotoxicity and cardiac dysfunction—Alzheimer’s disease of the heart? N. Engl. J. Med. 368, 455–464 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Ferrer I., Olivé M., Molecular pathology of myofibrillar myopathies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 10, e25 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

