A single dose of antibody-drug conjugate cures a stage 1 model of African trypanosomiasis
- PMID: 31120889
- PMCID: PMC6532856
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007373
A single dose of antibody-drug conjugate cures a stage 1 model of African trypanosomiasis
Abstract
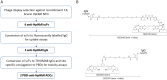
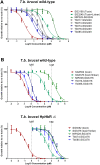
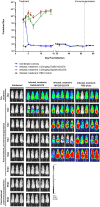
Infections of humans and livestock with African trypanosomes are treated with drugs introduced decades ago that are not always fully effective and often have severe side effects. Here, the trypanosome haptoglobin-haemoglobin receptor (HpHbR) has been exploited as a route of uptake for an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) that is completely effective against Trypanosoma brucei in the standard mouse model of infection. Recombinant human anti-HpHbR monoclonal antibodies were isolated and shown to be internalised in a receptor-dependent manner. Antibodies were conjugated to a pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) toxin and killed T. brucei in vitro at picomolar concentrations. A single therapeutic dose (0.25 mg/kg) of a HpHbR antibody-PBD conjugate completely cured a T. brucei mouse infection within 2 days with no re-emergence of infection over a subsequent time course of 77 days. These experiments provide a demonstration of how ADCs can be exploited to treat protozoal diseases that desperately require new therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
A.L.G.M., S.R., A.M.S., T.J.V. and R.M. are employees of Medimmune. F.D., C.S.B. and P.H. are employees of Spirogen. Toxins SG3199/SG3249 and SG3552/SG3376 are subject to international patents, WO 2011/130598 A1 and WO 2014/140862 A2, respectively.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemotherapeutic strategies against Trypanosoma brucei: drug targets vs. drug targeting.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(6):555-67. doi: 10.2174/138161207780162809. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17346174 Review.
-
Haptoglobin is dispensable for haemoglobin uptake by Trypanosoma brucei.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1441131. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1441131. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39114668 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of African trypanosomiasis with cordycepin and adenosine deaminase inhibitors in a mouse model.J Infect Dis. 2005 Nov 1;192(9):1658-65. doi: 10.1086/496896. Epub 2005 Sep 30. J Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16206083
-
The efficacy of ascofuranone in a consecutive treatment on Trypanosoma brucei brucei in mice.Parasitol Int. 2003 Jun;52(2):155-64. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5769(03)00012-6. Parasitol Int. 2003. PMID: 12798927
-
25 years of African trypanosome research: From description to molecular dissection and new drug discovery.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015 Mar-Apr;200(1-2):30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 25736427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of Antibody-Antibiotic Conjugates to Fight Bacterial Infections.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 7;13:835677. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.835677. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35330773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Novel Quinoline-Based Proteasome Inhibitors for Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT).J Med Chem. 2022 Sep 8;65(17):11776-11787. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00791. Epub 2022 Aug 22. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35993839 Free PMC article.
-
A receptor for the complement regulator factor H increases transmission of trypanosomes to tsetse flies.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 12;11(1):1326. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15125-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32165615 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides, Antibodies, Peptide Antibodies and More.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 13;20(24):6289. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246289. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31847088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in immunotherapies against infectious diseases.Immunother Adv. 2020 Nov 25;1(1):ltaa007. doi: 10.1093/immadv/ltaa007. eCollection 2021 Jan. Immunother Adv. 2020. PMID: 38626281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. Human African trypanosomiasis in Working to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases. First WHO report on neglected tropical diseases. 2010;1(1):82–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

