Clinical Value of Circulating Microribonucleic Acids miR-1 and miR-21 in Evaluating the Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure in Asymptomatic Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- PMID: 31109008
- PMCID: PMC6571732
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9050193
Clinical Value of Circulating Microribonucleic Acids miR-1 and miR-21 in Evaluating the Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure in Asymptomatic Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Abstract
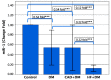
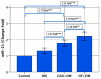
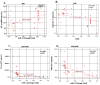
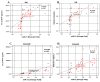
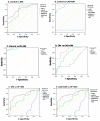
To investigate whether the circulating miR-1 (microRNA-1) and miR-21 expression might be used in the diagnosis of heart failure (HF) and silent coronary artery disease (SCAD) in asymptomatic type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients and to explore the relationship of these miRs with N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and galectin-3. One hundred thirty-five consecutive patients with T2DM and 45 matched control subjects were enrolled in the study. This study consisted of the following four groups: control group (mean age: 60.23 ± 6.27 years, female/male (F/M): 23/22); diabetic group (DM) (mean age: 61.50 ± 5.08, F/M: 23/22); DM + SCAD group (mean age: 61.61 ± 6.02, F/M: 20/25); and DM + acute HF group (mean age: 62.07 ± 5.26 years, F/M: 20/25). miR-1 was downregulated in the DM, CAD + DM and HF + DM groups by 0.54, 0.54, and 0.12 fold as compared with controls, respectively. The miR-1 levels were significantly lower in HF + DM than DM with 0.22 fold changes (p < 0.001); and in patients with CAD + DM group with 0.22 fold changes (p < 0.001). Similarly, miR-21 was overexpressed in patients with DM, CAD + DM, and HF + DM with 1.30, 1.79 and 2.21 fold changes as compared with controls, respectively. An interesting finding is that the miR-21 expression was significantly higher in the HF + DM group as compared with the CAD + DM group; miR-1 was negatively correlated with NT-proBNP (r = -0.891, p < 0.001) and galectin-3 (r = -0.886, p < 0.001) in the HF + DM group; and miR-21 showed a strongly positive correlation with (r = 0.734, p < 0.001) and galectin-3 (r = 0.764. p < 0.001) in the HF + DM group. These results suggest that the circulating decreased miR-1 and increased miR-21 expression are associated with NT-proBNP and galectin-3 levels in acute HF + DM. Especially the miR-21 expression might be useful in predicting the onset of acute HF in asymptomatic T2DM patients. The miR-21 expression is more valuable than the miR-1 expression in predicting cardiovascular events of acute HF and the combined analysis of miR-21 expression, galectin-3, and NT-proBNP can increase the predictive value of miR-21 expression.
Keywords: NT-proBNP; acute heart failure; asymptomatic type 2 diabetes mellitus; galectin-3; miRNA-1; miRNA-21; silent coronary artery disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circulating microribonucleic acids miR-1, miR-21 and miR-208a in patients with symptomatic heart failure: Preliminary results.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Dec;108(12):634-42. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26498537
-
Combined Use of Circulating miR-133a and NT-proBNP Improves Heart Failure Diagnostic Accuracy in Elderly Patients.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Dec 7;24:8840-8848. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911632. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30523241 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as candidate markers to distinguish heart failure in breathless patients.Eur J Heart Fail. 2013 Oct;15(10):1138-47. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hft078. Epub 2013 May 21. Eur J Heart Fail. 2013. PMID: 23696613
-
Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing for the diagnosis or exclusion of heart failure in patients with acute symptoms.Am J Cardiol. 2008 Feb 4;101(3A):29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.017. Am J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18243855 Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as predictive biomarkers of coronary artery diseases in type 2 diabetes patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 May;36(5):e24380. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24380. Epub 2022 Mar 29. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35349731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative biology of extracellular vesicles in diabetes mellitus and diabetic complications.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 1;12(3):1342-1372. doi: 10.7150/thno.65778. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35154494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential of Galectin-3 in Cardiovascular Diseases.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 29;12(1):46. doi: 10.3390/biom12010046. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 35053194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cell Type-Specific Functions of miR-21 in Cardiovascular Diseases.Front Genet. 2020 Nov 20;11:563166. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.563166. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33329700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic memory: mechanisms and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Feb 28;9(1):38. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01755-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38413567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics of the Pathogenesis and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.touchREV Endocrinol. 2023 May;19(1):46-53. doi: 10.17925/EE.2023.19.1.46. Epub 2023 Apr 13. touchREV Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37313245 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oremus M., McKelvie R., Don-Wauchope A., Santaguida P.L., Ali U., Balion C., Hill S., Booth R., Brown J.A., Bustamam A., et al. A systematic review of BNP and NT-proBNP in the management of heart failure: Overview and methods. Hear. Fail. Rev. 2014;19:413–419. doi: 10.1007/s10741-014-9440-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

