Sequential Immunization With Live-Attenuated Chimeric Hemagglutinin-Based Vaccines Confers Heterosubtypic Immunity Against Influenza A Viruses in a Preclinical Ferret Model
- PMID: 31105689
- PMCID: PMC6499175
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00756
Sequential Immunization With Live-Attenuated Chimeric Hemagglutinin-Based Vaccines Confers Heterosubtypic Immunity Against Influenza A Viruses in a Preclinical Ferret Model
Abstract
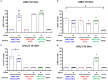
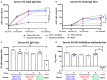
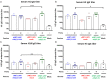
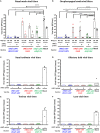
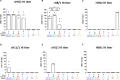
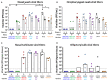
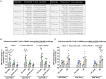
Due to continuous antigenic drift and occasional antigenic shift, influenza viruses escape from human adaptive immunity resulting in significant morbidity and mortality in humans. Therefore, to avoid the need for annual reformulation and readministration of seasonal influenza virus vaccines, we are developing a novel chimeric hemagglutinin (cHA)-based universal influenza virus vaccine, which is comprised of sequential immunization with antigens containing a conserved stalk domain derived from a circulating pandemic H1N1 strain in combination with "exotic" head domains. Here, we show that this prime-boost sequential immunization strategy redirects antibody responses toward the conserved stalk region. We compared the vaccine efficacy elicited by distinct vaccination approaches in the preclinical ferret model of influenza. All ferrets immunized with cHA-based vaccines developed stalk-specific and broadly cross-reactive antibody responses. Two consecutive vaccinations with live-attenuated influenza viruses (LAIV-LAIV) conferred superior protection against pH1N1 and H6N1 challenge infection. Sequential immunization with LAIV followed by inactivated influenza vaccine (LAIV-IIV regimen) also induced robust antibody responses. Importantly, the LAIV-LAIV immunization regimen also induced HA stalk-specific CD4+IFN-γ+ and CD8+IFN-γ+ effector T cell responses in peripheral blood that were recalled by pH1N1 viral challenge. The findings from this preclinical study suggest that an LAIV-LAIV vaccination regimen would be more efficient in providing broadly protective immunity against influenza virus infection as compared to other approaches tested here.
Keywords: chimeric hemagglutinin; ferret; heterosubtypic protection; live-attenuated influenza vaccine; stalk antibody; universal influenza virus vaccine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
T-cell-mediated cross-strain protective immunity elicited by prime-boost vaccination with a live attenuated influenza vaccine.Int J Infect Dis. 2014 Oct;27:37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.05.016. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Int J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25172265 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Influenza B Universal Vaccine Candidates Using the "Mosaic" Hemagglutinin Approach.J Virol. 2019 May 29;93(12):e00333-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00333-19. Print 2019 Jun 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30944178 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric Hemagglutinin-Based Live-Attenuated Vaccines Confer Durable Protective Immunity against Influenza A Viruses in a Preclinical Ferret Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jan 11;9(1):40. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9010040. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33440898 Free PMC article.
-
The Quest for a Truly Universal Influenza Vaccine.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Oct 10;9:344. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00344. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31649895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Approaches for The Development of Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccines.Viruses. 2019 Feb 22;11(2):190. doi: 10.3390/v11020190. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30813325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in the Development of Universal Influenza Vaccines.Viruses. 2020 Sep 17;12(9):1033. doi: 10.3390/v12091033. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32957468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Antigens for Universal Influenza Vaccine Development.Viruses. 2021 May 24;13(6):973. doi: 10.3390/v13060973. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34073996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced cross protection by hetero prime-boost vaccination with recombinant influenza viruses containing chimeric hemagglutinin-M2e epitopes.Virology. 2022 Jan;566:143-152. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2021.12.003. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Virology. 2022. PMID: 34929590 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and development of monoclonal antibodies for identification of ferret T follicular helper cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 21;11(1):1864. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81389-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33479388 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination With Viral Vectors Expressing Chimeric Hemagglutinin, NP and M1 Antigens Protects Ferrets Against Influenza Virus Challenge.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 21;10:2005. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02005. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31497029 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

