Pro-Angiogenic Actions of CMC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Rely on Selective Packaging of Angiopoietin 1 and 2, but Not FGF-2 and VEGF
- PMID: 31102187
- PMCID: PMC6941436
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-019-09891-6
Pro-Angiogenic Actions of CMC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Rely on Selective Packaging of Angiopoietin 1 and 2, but Not FGF-2 and VEGF
Abstract
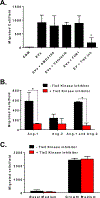
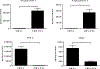
While the fundamental mechanism by which cardiac cell therapy mitigates ventricular dysfunction in the post ischemic heart remains poorly defined, donor cell paracrine signaling is presumed to be a chief contributor to the afforded benefits. Of the many bioactive molecules secreted by transplanted cells, extracellular vesicles (EVs) and their proteinaceous, nucleic acid, and lipid rich contents, comprise a heterogeneous assortment of prospective cardiotrophic factors-whose involvement in the activation of endogenous cardiac repair mechanism(s), including reducing fibrosis and promoting angiogenesis, have yet to be fully explained. In the current study we aimed to interrogate potential mechanisms by which cardiac mesenchymal stromal cell (CMC)-derived EVs contribute to the CMC pro-angiogenic paracrine signaling capacity in vitro. Vesicular transmission and biological activity of human CMC-derived EVs was evaluated in in vitro assays for human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) function, including EV uptake, cell survival, migration, tube formation, and intracellular pathway activation. HUVECs incubated with EVs exhibited augmented cell migration, tube formation, and survival under peroxide exposure; findings which paralleled enhanced activation of the archetypal pro-survival/pro-angiogenic pathways, STAT3 and PI3K-AKT. Cytokine array analyses revealed preferential enrichment of a subset of prototypical angiogenic factors, Ang-1 and Ang-2, in CMC EVs. Interestingly, pharmacologic inhibition of Tie2 in HUVECs, the cognate receptors of angiopoietins, efficiently attenuated CMC-EV-induced HUVEC migration. Further, in additional assays a Tie2 kinase inhibitor exhibited specificity to inhibit Ang-1-, but not Ang-2-, induced HUVEC migration. Overall, these findings suggest that the pro-angiogenic activities of CMC EVs are principally mediated by Ang-1-Tie2 signaling.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Angiopoietin; Cardiac Mesenchymal Cells; Endothelial Cells; Extracelluar Vesicles; Migration.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complementary actions of melatonin on angiogenic factors, the angiopoietin/Tie2 axis and VEGF, in co‑cultures of human endothelial and breast cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Jan;39(1):433-441. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6070. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29115538
-
IL-35 Inhibits Angiogenesis through VEGF/Ang2/Tie2 Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(5):1105-1116. doi: 10.1159/000453165. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27960151
-
Endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles induce pro-angiogenic responses in mesenchymal stem cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2024 May;14(5):740-755. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13650. Epub 2024 Mar 29. FEBS Open Bio. 2024. PMID: 37199081 Free PMC article.
-
The angiopoietin:Tie 2 interaction: a potential target for future therapies in human vascular disease.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Dec;24(6):579-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23838360 Review.
-
Angiopoietin/Tie2 signaling, tumor angiogenesis and inflammatory diseases.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:666-74. doi: 10.2741/1561. Print 2005 Jan 1. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15569607 Review.
Cited by
-
Delineating the role of extracellular vesicles in cancer metastasis: A comprehensive review.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 19;13:966661. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.966661. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36059497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes in regenerative medicine and cancer; overview of development, challenges, and opportunities.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 May 21;12(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02378-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34020704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenic Effects of Human Dental Pulp and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and their Extracellular Vesicles.Cells. 2020 Jan 28;9(2):312. doi: 10.3390/cells9020312. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32012900 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic combinations of exosomes alongside cancer stem cells (CSCs) and of CSC-derived exosomes (CSCEXs) in cancer therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 5;24(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03514-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39369258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Pericyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Vascular and Neurological Health.Cells. 2022 Oct 2;11(19):3108. doi: 10.3390/cells11193108. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

