Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome
- PMID: 31092918
- PMCID: PMC7039709
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1192-5
Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome
Abstract
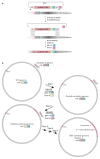
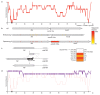
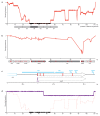
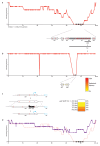
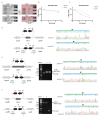
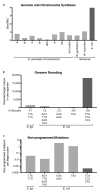
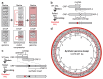
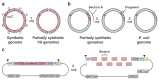
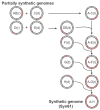
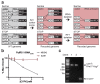
Nature uses 64 codons to encode the synthesis of proteins from the genome, and chooses 1 sense codon-out of up to 6 synonyms-to encode each amino acid. Synonymous codon choice has diverse and important roles, and many synonymous substitutions are detrimental. Here we demonstrate that the number of codons used to encode the canonical amino acids can be reduced, through the genome-wide substitution of target codons by defined synonyms. We create a variant of Escherichia coli with a four-megabase synthetic genome through a high-fidelity convergent total synthesis. Our synthetic genome implements a defined recoding and refactoring scheme-with simple corrections at just seven positions-to replace every known occurrence of two sense codons and a stop codon in the genome. Thus, we recode 18,214 codons to create an organism with a 61-codon genome; this organism uses 59 codons to encode the 20 amino acids, and enables the deletion of a previously essential transfer RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Construction of an Escherichia coli genome with fewer codons sets records.Nature. 2019 May;569(7757):492-494. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-01584-x. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31097820 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Defining synonymous codon compression schemes by genome recoding.Nature. 2016 Nov 3;539(7627):59-64. doi: 10.1038/nature20124. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27776354 Free PMC article.
-
Recoded organisms engineered to depend on synthetic amino acids.Nature. 2015 Feb 5;518(7537):89-93. doi: 10.1038/nature14095. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25607356 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the limits of genetic recoding in essential genes.Science. 2013 Oct 18;342(6156):361-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1241460. Science. 2013. PMID: 24136967
-
Recent advances in genetic code engineering in Escherichia coli.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2012 Oct;23(5):751-7. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.12.027. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22237016 Review.
-
Experimental challenges of sense codon reassignment: an innovative approach to genetic code expansion.FEBS Lett. 2014 Jan 31;588(3):383-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.039. Epub 2013 Dec 12. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24333334 Review.
Cited by
-
Application and Technical Challenges in Design, Cloning, and Transfer of Large DNA.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;10(12):1425. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10121425. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adding α,α-disubstituted and β-linked monomers to the genetic code of an organism.Nature. 2024 Jan;625(7995):603-610. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06897-6. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38200312 Free PMC article.
-
Genomically recoded Escherichia coli with optimized functional phenotypes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 29:2024.08.29.610322. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.29.610322. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39257802 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Sc3.0: revamping and minimizing the yeast genome.Genome Biol. 2020 Aug 13;21(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02130-z. Genome Biol. 2020. PMID: 32791980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Chemical Reaction Models in Synthetic Promoter Design in Bacteria.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2844:3-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4063-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39068329
References
-
- Crick FH, Barnett L, Brenner S, Watts-Tobin RJ. General nature of the genetic code for proteins. Nature. 1961;192:1227–1232. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen MA, Pedersen S. Absolute in vivo translation rates of individual codons in Escherichia coli. The two glutamic acid codons GAA and GAG are translated with a threefold difference in rate. J Mol Biol. 1991;222:265–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

