Third BIR domain of XIAP binds to both Cu(II) and Cu(I) in multiple sites and with diverse affinities characterized at atomic resolution
- PMID: 31092843
- PMCID: PMC6520397
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42875-7
Third BIR domain of XIAP binds to both Cu(II) and Cu(I) in multiple sites and with diverse affinities characterized at atomic resolution
Abstract
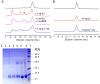
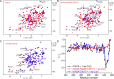
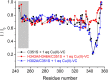
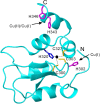
The X-chromosome linked inhibitor of apoptosis, XIAP, is mainly known as the inhibitor of caspases by direct interaction with caspases with its baculoviral IAP repeat (BIR) domains. XIAP has three BIR domains and each BIR domain contains a zinc binding site, normally known as zinc finger motif. Recent studies showed that XIAP is involved in copper homeostasis in cells and the BIR domains bind copper ion. However, structural details of the second and third BIR domain, BIR2 and BIR3, in XIAP, with copper as well as the binding modes are not known. In the present work we characterize the structural properties of BIR3 in solution by high resolution NMR and other biophysical techniques. The interaction of BIR3 with copper both in vitro and in cell lysates was analyzed. Our results show that BIR3 is able to form stable complexes both with Cu(II) and Cu(I), whereas zinc binding site is not affected and zinc retains tightly bound in the zinc finger during these interactions. Surprisingly, BIR3 has multiple binding sites for Cu(II) and Cu(I) but with varied binding affinities. In addition, the solvent exposed Cys351 is readily oxidized by Cu(II) resulting an intermolecular disulfide bond either between two BIR3 molecules or a mixed disulfide bond with glutathione in cell lysates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Copper-binding properties of the BIR2 and BIR3 domains of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.J Inorg Biochem. 2014 Nov;140:104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.07.010. Epub 2014 Jul 22. J Inorg Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25105866
-
Solution structure and interaction with copper in vitro and in living cells of the first BIR domain of XIAP.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 30;7(1):16630. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16723-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29192194 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of both the second and third BIR domains for the relief of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated caspase inhibition by Smac.J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 5;278(49):49517-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310061200. Epub 2003 Sep 25. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 14512414
-
Targeting XIAP for the treatment of malignancy.Cell Death Differ. 2006 Feb;13(2):179-88. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401826. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16322751 Review.
-
Targeting the BIR Domains of Inhibitor of Apoptosis (IAP) Proteins in Cancer Treatment.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Jan 25;17:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.01.009. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30766663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Movement Disorder in Copper Toxicity Rat Model: Role of Inflammation and Apoptosis in the Corpus Striatum.Neurotox Res. 2020 Apr;37(4):904-912. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00140-9. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 31811585
-
SMAC Mimetics for the Treatment of Lung Carcinoma: Present Development and Future Prospects.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(14):1334-1352. doi: 10.2174/0113895575269644231120104501. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38275029 Review.
-
Disruption of zinc (II) binding and dimeric protein structure of the XIAP-RING domain by copper (I) ions.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2023 Aug;28(5):485-494. doi: 10.1007/s00775-023-02002-4. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37268744
-
The expanded inhibitor of apoptosis gene family in oysters possesses novel domain architectures and may play diverse roles in apoptosis following immune challenge.BMC Genomics. 2022 Mar 12;23(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08233-6. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35279090 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

