Additive effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus L-92 on children with atopic dermatitis concomitant with food allergy
- PMID: 31089460
- PMCID: PMC6494655
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2019.9.e18
Additive effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus L-92 on children with atopic dermatitis concomitant with food allergy
Abstract
Background: Atopic dermatitis (AD) in infants is often related to food allergies (FA). The beneficial effects of lactic acid bacteria towards allergic diseases have been reported, but there are few reports on their effect and preferable dosages on AD in young children with concomitant FA.
Objective: To examine additional effects of two different dose of paraprobiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus L-92 (L-92) on the clinical treatment in young children afflicted by AD with diagnosed or suspected FA.
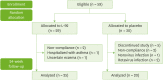
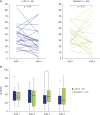
Methods: Fifty-nine AD young children from 10 months to 3 years old, with FA or who had not started to ingest specific food(s) because of high specific IgE levels, were recruited and randomly allocated into L-92 group (daily intake of 20 mg L-92/day) and placebo group. Participants were given test sample with conventional treatment for AD over a 24-week period. The severity of eczema was evaluated using SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index before intervention, and at 4, 12, and 24 weeks after intervention.
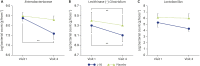
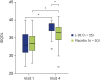
Results: After 24 weeks of intervention, a significant decrease in SCORAD was observed only in the L-92 group when compared with the baseline values. Significant decreases in thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) and total IgE were also detected 24 weeks after intake in the L-92 group compared with the placebo group.
Conclusion: It was suggested that intake of sufficient amounts of L-92 works as an adjunctive treatment of young children afflicted by AD with diagnosed or suspected FA.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Food sensitivity; Lactobacillus acidophilus.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of synbiotic supplementation on children with atopic dermatitis: an observational prospective study.Eur J Pediatr. 2018 Dec;177(12):1851-1858. doi: 10.1007/s00431-018-3253-4. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Eur J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30259127 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of prolonged ingestion of Lactobacillus acidophilus L-92 in adult patients with atopic dermatitis.J Dairy Sci. 2016 Jul;99(7):5039-5046. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-10605. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Dairy Sci. 2016. PMID: 27108169
-
Probiotics for the treatment or prevention of atopic dermatitis: a review of the evidence from randomized controlled trials.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9(2):93-103. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200809020-00002. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18284263 Review.
-
Effects of Lactobacillus pentosus in Children with Allergen-Sensitized Atopic Dermatitis.J Korean Med Sci. 2020 May 11;35(18):e128. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e128. J Korean Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32383366 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Probiotics in the treatment and prevention of allergies in children.Biosci Microflora. 2011;30(4):119-28. doi: 10.12938/bifidus.30.119. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Biosci Microflora. 2011. PMID: 25045317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary Interventions in Atopic Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Scoping Review and Analysis.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2024;185(6):545-589. doi: 10.1159/000535903. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38442688 Free PMC article.
-
Prebiotic effects of commercial apple juice in high-fat diet fed rat.BMC Res Notes. 2024 Sep 5;17(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13104-024-06907-4. BMC Res Notes. 2024. PMID: 39237963 Free PMC article.
-
Skin Dialogues in Atopic Dermatitis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Aug 4;12(8):1889. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12081889. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neglected Microbial Components of Commercial Probiotic Formulations.Microorganisms. 2020 Aug 3;8(8):1177. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8081177. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32756409 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Strain Probiotic Lactobacilli for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 17;15(4):1256. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041256. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Finlay AY. Quality of life in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45(1 Suppl):S64–S66. - PubMed
-
- Chamlin SL, Frieden IJ, Williams ML, Chren MM. Effects of atopic dermatitis on young American children and their families. Pediatrics. 2004;114:607–611. - PubMed
-
- Werfel T, Ballmer-Weber B, Eigenmann PA, Niggemann B, Rancé F, Turjanmaa K, Worm M. Eczematous reactions to food in atopic eczema: position paper of the EAACI and GA2LEN. Allergy. 2007;62:723–728. - PubMed
-
- Tsakok T, Marrs T, Mohsin M, Baron S, du Toit G, Till S, Flohr C. Does atopic dermatitis cause food allergy? A systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:1071–1078. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
