Selective Kinase Inhibition Shows That Bur1 (Cdk9) Phosphorylates the Rpb1 Linker In Vivo
- PMID: 31085683
- PMCID: PMC6639251
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00602-18
Selective Kinase Inhibition Shows That Bur1 (Cdk9) Phosphorylates the Rpb1 Linker In Vivo
Abstract
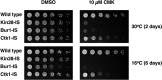
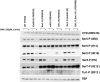
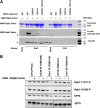
Cyclin-dependent kinases play multiple roles in RNA polymerase II transcription. Cdk7/Kin28, Cdk9/Bur1, and Cdk12/Ctk1 phosphorylate the polymerase and other factors to drive the dynamic exchange of initiation and elongation complex components over the transcription cycle. We engineered strains of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae for rapid, specific inactivation of individual kinases by addition of a covalent inhibitor. While effective, the sensitized kinases can display some idiosyncrasies, and inhibition can be surprisingly transient. As expected, inhibition of Cdk7/Kin28 blocked phosphorylation of the Rpb1 C-terminal domain heptad repeats at serines 5 and 7, the known target sites. However, serine 2 phosphorylation was also abrogated, supporting an obligatory sequential phosphorylation mechanism. Consistent with our previous results using gene deletions, Cdk12/Ctk1 is the predominant kinase responsible for serine 2 phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of the Rpb1 linker enhances binding of the Spt6 tandem SH2 domain, and here we show that Bur1/Cdk9 is the kinase responsible for these modifications in vivo.
Keywords: Cdk9; P-TEFb; RNA polymerase II; Rpb1; Spt6.
Copyright © 2019 Chun et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of the Pol II CTD by KIN28 enhances BUR1/BUR2 recruitment and Ser2 CTD phosphorylation near promoters.Mol Cell. 2009 Mar 27;33(6):752-62. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.02.018. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19328068 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylases and phosphorylated polymerase II C-terminal domain recruit Spt6 for cotranscriptional histone reassembly.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Nov 15;34(22):4115-29. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00695-14. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25182531 Free PMC article.
-
CDK12 is a transcription elongation-associated CTD kinase, the metazoan ortholog of yeast Ctk1.Genes Dev. 2010 Oct 15;24(20):2303-16. doi: 10.1101/gad.1968210. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20952539 Free PMC article.
-
Bur1/Bur2 and the Ctk complex in yeast: the split personality of mammalian P-TEFb.Cell Cycle. 2006 May;5(10):1066-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.10.2769. Epub 2006 May 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16721054 Review.
-
RNA polymerase II transcription elongation and Pol II CTD Ser2 phosphorylation: A tail of two kinases.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):224-36. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29347. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24879308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrator endonuclease drives promoter-proximal termination at all RNA polymerase II-transcribed loci.Mol Cell. 2022 Nov 17;82(22):4232-4245.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.10.004. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 36309014 Free PMC article.
-
Polo kinase recruitment via the constitutive centromere-associated network at the kinetochore elevates centromeric RNA.PLoS Genet. 2020 Aug 18;16(8):e1008990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008990. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32810142 Free PMC article.
-
Structural advances in transcription elongation.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022 Aug;75:102422. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102422. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 35816930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction between the Spt6-tSH2 domain and Rpb1 affects multiple functions of RNA Polymerase II.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 25;50(2):784-802. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1262. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34967414 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the Pol II transcription cycle and derailing cancer with CDK inhibitors.Nat Chem Biol. 2020 Jul;16(7):716-724. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0563-4. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Nat Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 32572259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
