Baishouwu Extract Suppresses the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 31068809
- PMCID: PMC6491767
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00389
Baishouwu Extract Suppresses the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
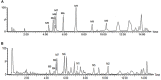
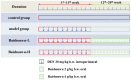
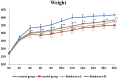
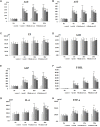
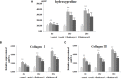
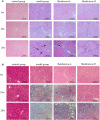
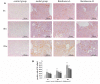
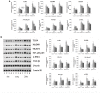
Purpose: The root of Cynanchum auriculatum Royle ex Wight, known as Baishouwu, has been widely used for a tonic supplement since ancient times. The current study was performed to explore the effect of Baishouwu extract on the development of experimental hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the potential mechanism involved. Methods: Rats were injected diethylnitrosamine (DEN) to initiate the multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. Animals were treated concurrently with Baishouwu extract given daily by oral gavage for 20 weeks to evaluate its protective effects. Time series sera and organ samples from each group were collected to evaluate the effect of Baishouwu extract on hepatic carcinogenesis. Results: It was found that Baishouwu extract pretreatment successfully attenuated liver injury induced by DEN, as shown by decreased levels of serum biochemical indicators (AST, ALT, ALP, TP, and T-BIL). Administration of Baishouwu extract inhibited the fibrosis-related index in serum and live tissue, respectively from inflammation stage to HCC stage after DEN treatment. It significantly reduced the incidence and multiplicity of DEN-induced HCC development in a dose-dependent manner. Macroscopic and microscopic features suggested that pretreatment with Baishouwu extract for 20 weeks was effective in inhibiting DEN-induced inflammation, liver fibrosis, and HCC. Furthermore, TLR4 overexpression induced by DEN was decreased by Baishouwu extract, leading to the markedly down-regulated levels of MyD88, TRAF6, NF-κB p65, TGF-β1 and α-SMA in hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocarcinoma. Conclusion: In conclusion, Baishouwu extract exhibited potent effect on the development of HCC by altering TLR4/MyD88/ NF-κB signaling pathway in the sequence of hepatic inflammation-fibrosis-cancer, which provided novel insights into the mechanism of Baishouwu extract as a candidate for the pretreatment of HCC in the future.
Keywords: Baishouwu extract; TLR4; hepatocellular carcinoma; inflammation-fibrosis-cancer axis; pretreatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatic inflammation-fibrosis-cancer axis in the rat hepatocellular carcinoma induced by diethylnitrosamine.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 May;143(5):821-834. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2364-z. Epub 2017 Feb 25. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28238064
-
[Effects of total C-21 steroidal glucosides from Cynanchum auriculatum on oxidative stress pathway in mice with liver injury].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Jul;44(14):2960-2965. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190426.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31602840 Chinese.
-
Total C-21 Steroidal Glycosides From Baishouwu Ameliorate Hepatic and Renal Fibrosis by Regulating IL-1β/MyD88 Inflammation Signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 26;12:775730. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.775730. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34764877 Free PMC article.
-
Cynanchum bungei Decne and its two related species for "Baishouwu": A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Oct 28;243:112110. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112110. Epub 2019 Jul 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31351190 Review.
-
The antitumour activity of C21 steroidal glycosides and their derivatives of Baishouwu: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115300. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115300. Epub 2022 Apr 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35430288 Review.
Cited by
-
Long noncoding RNA MyD88 functions as a promising diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 30;14:938102. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.938102. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36793272 Free PMC article.
-
Calotropis gigantea stem bark extracts inhibit liver cancer induced by diethylnitrosamine.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 15;12(1):12151. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16321-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35840761 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative sub-chronic toxicity studies in rats of two indistinguishable herbal plants, Cynanchum wilfordii (Maxim.) Hemsley and Cynanchum auriculatum Royle ex Wight.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 19;31(6):759-766. doi: 10.1007/s10068-022-01072-5. eCollection 2022 Jun. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35646417 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 13 Contributes to Tumor Growth and Metastasis via Enhancing the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Gene 88/Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 19;8:587389. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.587389. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195243 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid loaded silica nanoemulsion attenuates hepatic inflammation through the enhancement of cell membrane components.Biol Proced Online. 2022 Sep 7;24(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12575-022-00173-z. Biol Proced Online. 2022. PMID: 36071378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansil P. N., Nitha A., Prabha S. P., Latha M. S. (2014). Curative effect of Amorphophallus campanulatus (Roxb.) Blume. tuber on N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 33 205–218. 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2014011320 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

