Flaxseed Lignans as Important Dietary Polyphenols for Cancer Prevention and Treatment: Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, and Molecular Targets
- PMID: 31060335
- PMCID: PMC6630319
- DOI: 10.3390/ph12020068
Flaxseed Lignans as Important Dietary Polyphenols for Cancer Prevention and Treatment: Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, and Molecular Targets
Abstract
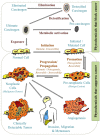
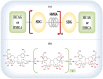
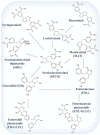
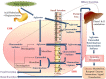
Cancer causes considerable morbidity and mortality across the world. Socioeconomic, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to the increasing cancer prevalence, bespeaking a need for effective prevention and treatment strategies. Phytochemicals like plant polyphenols are generally considered to have anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory effects, which explain their promotion for human health. The past several decades have contributed to a growing evidence base in the literature that demonstrate ability of polyphenols to modulate multiple targets of carcinogenesis linking models of cancer characteristics (i.e., hallmarks and nutraceutical-based targeting of cancer) via direct or indirect interaction or modulation of cellular and molecular targets. This evidence is particularly relevant for the lignans, an ubiquitous, important class of dietary polyphenols present in high levels in food sources such as flaxseed. Literature evidence on lignans suggests potential benefit in cancer prevention and treatment. This review summarizes the relevant chemical and pharmacokinetic properties of dietary polyphenols and specifically focuses on the biological targets of flaxseed lignans. The consolidation of the considerable body of data on the diverse targets of the lignans will aid continued research into their potential for use in combination with other cancer chemotherapies, utilizing flaxseed lignan-enriched natural products.
Keywords: Cellular/molecular targets; Chemopreventive; Chemotherapeutic; Dietary polyphenols; Flaxseed lignans; Hallmarks of cancer; Pharmacokinetics; Phytochemicals; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses or interpretation, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish this review.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anticancer potential of flaxseed lignans, their metabolites and synthetic counterparts in relation with molecular targets: current challenges and future perspectives.Food Funct. 2023 Mar 6;14(5):2286-2303. doi: 10.1039/d2fo02208g. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 36820797 Review.
-
The fate of flaxseed-lignans after oral administration: A comprehensive review on its bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and food design strategies for optimal application.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(13):4312-4330. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2140643. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36345888 Review.
-
Flaxseed: a potential source of food, feed and fiber.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2011 Mar;51(3):210-22. doi: 10.1080/10408390903537241. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21390942 Review.
-
The legitimacy of using dietary supplement diglycoside secoisolariciresinol (SDG) from flaxseed in cancer.Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2021;72(1):9-20. doi: 10.32394/rpzh.2021.0144. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2021. PMID: 33882661 Review.
-
Influence of Flaxseed Lignan Supplementation to Older Adults on Biochemical and Functional Outcome Measures of Inflammation.J Am Coll Nutr. 2017 Nov-Dec;36(8):646-653. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2017.1342213. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Am Coll Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28922068 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Metabolic Profiling of Synechocystis sp. Extract Encapsulated in Nano-Liposomes and Nano-Niosomes Using LC-MS, Complemented by Molecular Docking Studies.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;13(8):581. doi: 10.3390/biology13080581. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194519 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Yield Characteristics, Chemical Composition, Lignans Content and Antioxidant Potential of Experimentally Grown Six Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) Cultivars.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024 Mar;79(1):159-165. doi: 10.1007/s11130-023-01136-9. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38236453
-
The Untargeted Phytochemical Profile of Three Meliaceae Species Related to In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Anti-Virulence Activity against MRSA Isolates.Molecules. 2022 Jan 10;27(2):435. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020435. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056761 Free PMC article.
-
Linum lewisii Adventitious and Hairy-Roots Cultures as Lignan Plant Factories.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 5;11(8):1526. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081526. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009248 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role of Dietary Phenolic Compounds in the Prevention and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Reports.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 6;17(5):590. doi: 10.3390/ph17050590. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

