Carboxypeptidase A4 promotes proliferation and stem cell characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31058377
- PMCID: PMC6540673
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12315
Carboxypeptidase A4 promotes proliferation and stem cell characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
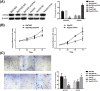
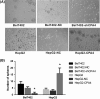
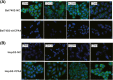
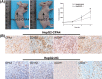
Carboxypeptidase A4 (CPA4), a member of the metallo-carboxypeptidase family, is overexpressed in liver cancer and is associated with cancer progression. The role of CPA4 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the relevance of CPA4 to the proliferation and expression of stem cell characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Western blot analysis showed high CPA4 expression in the liver cancer cell line Bel7402 and low expression in HepG2 cells. Knock-down of CPA4 decreased cancer cell proliferation as detected by MTT and clone formation assays. The serum-free culture system revealed that downregulated CPA4 suppressed the sphere formation capacities of tumour cells. However, upregulated CPA4 increased the proliferation and sphere formation capacity. In addition, the protein expression of CD133, ALDH1 and CD44 also increased in cells with upregulated CPA4. In vivo, the overexpression of CPA4 in tumour cells that were subcutaneously injected into nude mice markedly increased the growth of the tumours. These data suggest that CPA4 expression leads to poor prognoses by regulating tumour proliferation and the expression of stem cell characteristics and may therefore serve as a potential therapeutic target of HCC.
Keywords: cancer stem cell; carboxypeptidase A4; hepatocellular carcinoma; proliferation.
© 2019 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2019 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carboxypeptidase A4 negatively correlates with p53 expression and regulates the stemness of breast cancer cells.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 18;18(8):1753-1759. doi: 10.7150/ijms.54954. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746592 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage-Induced Carboxypeptidase A4 Promotes the Progression of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer.Thyroid. 2024 Sep;34(9):1150-1162. doi: 10.1089/thy.2023.0427. Epub 2024 May 13. Thyroid. 2024. PMID: 38666696
-
Downregulation of CPA4 inhibits non small-cell lung cancer growth by suppressing the AKT/c-MYC pathway.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Nov;58(11):2026-2039. doi: 10.1002/mc.23095. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 31397502 Free PMC article.
-
miR-589-5p inhibits MAP3K8 and suppresses CD90+ cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 11;35(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0452-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27835990 Free PMC article.
-
Liver cancer: the role of stem cells.Cell Prolif. 2005 Dec;38(6):407-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2005.00354.x. Cell Prolif. 2005. PMID: 16300653 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carboxypeptidase A4 negatively correlates with p53 expression and regulates the stemness of breast cancer cells.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 18;18(8):1753-1759. doi: 10.7150/ijms.54954. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746592 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxypeptidase A4 promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through activating PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling.Biosci Rep. 2020 May 29;40(5):BSR20200669. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200669. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32347291 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic role of LGR6 overexpression induced by aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling in lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2024 Jan;15(2):131-141. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15169. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38014454 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of carboxypeptidase A4 (CPA4) inhibits gastric cancer cell progression via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Dec;13(6):2823-2831. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-987. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36636089 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer stem cells in esophageal squamous cell cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):5022-5032. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10900. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31612013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

