Polymorphisms in Dopaminergic Genes in Schizophrenia and Their Implications in Motor Deficits and Antipsychotic Treatment
- PMID: 31057354
- PMCID: PMC6479209
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00355
Polymorphisms in Dopaminergic Genes in Schizophrenia and Their Implications in Motor Deficits and Antipsychotic Treatment
Abstract
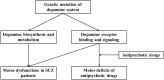
Dopaminergic system dysfunction is involved in schizophrenia (SCZ) pathogenesis and can mediate SCZ-related motor disorders. Recent studies have gradually revealed that SCZ susceptibility and the associated motor symptoms can be mediated by genetic factors, including dopaminergic genes. More importantly, polymorphisms in these genes are associated with both antipsychotic drug sensitivity and adverse effects. The study of genetic polymorphisms in the dopaminergic system may help to optimize individualized drug strategies for SCZ patients. This review summarizes the current progress about the involvement of the dopamine system in SCZ-associated motor disorders and the motor-related adverse effects after antipsychotic treatment, with a special focus on polymorphisms in dopaminergic genes. We hypothesize that the genetic profile of the dopaminergic system mediates both SCZ-associated motor deficits associated and antipsychotic drug-related adverse effects. The study of dopaminergic gene polymorphisms may help to predict drug efficacy and decrease adverse effects, thereby optimizing treatment strategies.
Keywords: antipsychotic drugs; dopaminergic transmission; gene polymorphism; pharmacogenetics; schizophrenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between the serotonin 2A receptor gene and tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenia.Mol Psychiatry. 2001 Mar;6(2):225-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000842. Mol Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11317227
-
Genetic Variants Within Key Nodes of the Cascade of Antipsychotic Mechanisms: Effects on Antipsychotic Response and Schizophrenia Psychopathology in a Naturalistic Treatment Setting in Two Independent Korean and Italian Samples.Adv Ther. 2017 Jun;34(6):1482-1497. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0555-2. Epub 2017 May 16. Adv Ther. 2017. PMID: 28508933
-
Some dopaminergic genes polymorphisms are not associated with response to antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenic patients.Pharmacol Rep. 2012;64(3):528-35. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(12)70848-4. Pharmacol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22814006 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacogenetics and antipsychotic treatment response.Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2015;36(1):53-67. Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2015. PMID: 26076775 Review.
-
Dopaminergic dysbalance in distinct basal ganglia neurocircuits: implications for the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.Neurotox Res. 2006 Dec;10(3-4):167-79. doi: 10.1007/BF03033354. Neurotox Res. 2006. PMID: 17197367 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating the Roles of Midbrain Dopamine Circuits in Behavior and Neuropsychiatric Disease.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 7;9(6):647. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060647. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34200134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of neural mechanotransduction response in human traumatic brain injury organoid model.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 19;13(1):13536. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40431-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37598247 Free PMC article.
-
Association of DRD2, DRD4 and COMT genes variants and their gene-gene interactions with antipsychotic treatment response in patients with schizophrenia.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 25;23(1):781. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05292-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37880658 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Dopamine D3 Receptors, Dysbindin, and Their Functional Interaction in the Expression of Key Genes for Neuroplasticity and Neuroinflammation in the Mouse Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 12;24(10):8699. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108699. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abi-Dargham A. (2014). Dopamine dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 160, e6–e7. 10.1016/j.schres.2014.09.069 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources