Quality assessment of systematic reviews and meta-analyses published in Saudi journals from 1997 to 2017
- PMID: 31056617
- PMCID: PMC6535175
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2019.5.23690
Quality assessment of systematic reviews and meta-analyses published in Saudi journals from 1997 to 2017
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the quality of the meta-analyses (MAs) and systematic reviews (SRs) in Saudi journals indexed in PubMed using 2 scales: A MeaSurement tool to assess systematic reviews (AMSTAR) and the overview quality assessment questionnaire (OQAQ).
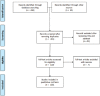
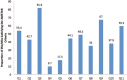
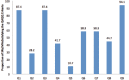
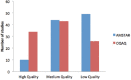
Methods: This study focused on SRs/MAs published in 8 Saudi journals. We investigated, screened and extracted the data, which included recording the main topic of each SRs/MAs and the date of publication. Furthermore, we assessed the quality of each included SRs/MAs using the AMSTAR and the OQAQ. The reviews concluded in January 2018. Results: The search uncovered 201 unique articles; of these, the researchers screened 110 full texts and included 103 in this review. Most of the included studies were published in Saudi Medical Journal (50 articles, 48.5%), followed by Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology (21 articles, 20.4%), and Annals of Saudi Medicine (16 articles, 15.5%) . The main topics in these published articles were gastroenterology (20 articles, 19.5%), followed by oncology (14 articles, 13.7%), and pharmacology (9 articles, 8.7%). The AMSTAR and the OQAQ scales showed that most SRs/MAs were of medium quality.
Conclusion: Quality of SRs and MAs published in Saudi journals was distributed in all categories (low, medium, and high) and it can be improved using critical evaluation by authors, journal editors, and readers. PROSPERO REG. NO. CRD: 42018102210.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reporting Quality of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Otorhinolaryngologic Articles Based on the PRISMA Statement.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0136540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136540. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Quality of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses in Erectile Dysfunction Treatment and Management Published in the Sexual Medicine Literature.J Sex Med. 2019 Mar;16(3):394-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.01.009. Epub 2019 Feb 14. J Sex Med. 2019. PMID: 30773501
-
Methodological Quality Assessment of Meta-analyses and Systematic Reviews of the Relationship Between Periodontal and Systemic Diseases.J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2019 Jun;19(2):131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jebdp.2018.12.003. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2019. PMID: 31326045
-
Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses Published in High-Impact Otolaryngology Journals.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Nov;163(5):892-905. doi: 10.1177/0194599820924621. Epub 2020 May 26. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32450783
-
Epidemiology, quality, and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of nursing interventions published in Chinese journals.Nurs Outlook. 2015 Jul-Aug;63(4):446-455.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.outlook.2014.11.020. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Nurs Outlook. 2015. PMID: 26187084 Review.
Cited by
-
How to Write a Systematic Review: A Narrative Review.Int J Prev Med. 2021 Mar 29;12:27. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_60_20. eCollection 2021. Int J Prev Med. 2021. PMID: 34249276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evidence-Based Medicine. A new approach to teaching the practice of medicine. Jama. 1992;268:2420–2425. - PubMed
-
- Oxman AD, Guyatt GH. Validation of an index of the quality of review articles. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991;44:1271–1278. - PubMed
-
- Shea BJ, Hamel C, Wells GA, Bouter LM, Kristjansson E, Grimshaw J, et al. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:1013–1020. - PubMed
-
- Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Blackmore H, Kitas GD. Writing a narrative biomedical review:considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol Int. 2011;31:1409–1417. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

