Partial ligand-receptor engagement yields functional bias at the human complement receptor, C5aR1
- PMID: 31036565
- PMCID: PMC6579481
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007485
Partial ligand-receptor engagement yields functional bias at the human complement receptor, C5aR1
Abstract
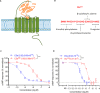
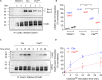
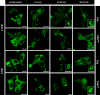
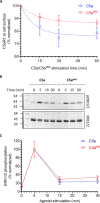
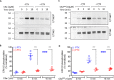
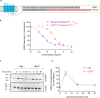
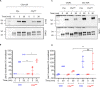
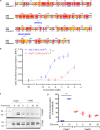
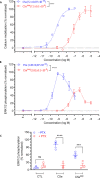
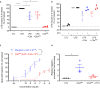
The human complement component, C5a, binds two different seven-transmembrane receptors termed C5aR1 and C5aR2. C5aR1 is a prototypical G-protein-coupled receptor that couples to the Gαi subfamily of heterotrimeric G-proteins and β-arrestins (βarrs) following C5a stimulation. Peptide fragments derived from the C terminus of C5a can still interact with the receptor, albeit with lower affinity, and can act as agonists or antagonists. However, whether such fragments might display ligand bias at C5aR1 remains unexplored. Here, we compare C5a and a modified C-terminal fragment of C5a, C5apep, in terms of G-protein coupling, βarr recruitment, endocytosis, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation at the human C5aR1. We discover that C5apep acts as a full agonist for Gαi coupling as measured by cAMP response and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation, but it displays partial agonism for βarr recruitment and receptor endocytosis. Interestingly, C5apep exhibits full-agonist efficacy with respect to inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 secretion in human macrophages, but its ability to induce human neutrophil migration is substantially lower compared with C5a, although both these responses are sensitive to pertussis toxin treatment. Taken together, our data reveal that compared with C5a, C5apep exerts partial efficacy for βarr recruitment, receptor trafficking, and neutrophil migration. Our findings therefore uncover functional bias at C5aR1 and also provide a framework that can potentially be extended to chemokine receptors, which also typically interact with chemokines through a biphasic mechanism.
Keywords: G-protein–coupled receptor (GPCR); arrestin; cell signaling; complement; signal transduction.
© 2019 Pandey et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ras-Related Protein Rab5a Regulates Complement C5a Receptor Trafficking, Chemotaxis, and Chemokine Secretion in Human Macrophages.J Innate Immun. 2023;15(1):468-484. doi: 10.1159/000530012. Epub 2023 Mar 7. J Innate Immun. 2023. PMID: 36882040 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of functionally selective C5aR2 ligands: novel modulators of C5a signalling.Immunol Cell Biol. 2016 Sep;94(8):787-95. doi: 10.1038/icb.2016.43. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Immunol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27108698
-
C5aR2 receptor: The genomic twin of the flamboyant C5aR1.J Cell Biochem. 2022 Nov;123(11):1841-1856. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30320. Epub 2022 Aug 17. J Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35977039
-
Emerging Insights into the Structure and Function of Complement C5a Receptors.Trends Biochem Sci. 2020 Aug;45(8):693-705. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.04.004. Epub 2020 May 10. Trends Biochem Sci. 2020. PMID: 32402749 Review.
-
The critical role of C5a as an initiator of neutrophil-mediated autoimmune inflammation of the joint and skin.Semin Immunol. 2018 Jun;37:21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Semin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29602515 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanism of distinct chemokine engagement and functional divergence of the human Duffy antigen receptor.Cell. 2024 Aug 22;187(17):4751-4769.e25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.005. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39089252 Free PMC article.
-
The "C3aR Antagonist" SB290157 is a Partial C5aR2 Agonist.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 21;11:591398. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.591398. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33551801 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide/Receptor Co-evolution Explains the Lipolytic Function of the Neuropeptide TLQP-21.Cell Rep. 2019 Sep 3;28(10):2567-2580.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.101. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31484069 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of anaphylatoxin binding, activation, and signaling bias at complement receptors.Cell. 2023 Oct 26;186(22):4956-4973.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.020. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37852260 Free PMC article.
-
Structural biology of complement receptors.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 11;14:1239146. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1239146. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37753090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siciliano S. J., Rollins T. E., DeMartino J., Konteatis Z., Malkowitz L., Van Riper G., Bondy S., Rosen H., and Springer M. S. (1994) Two-site binding of C5a by its receptor: an alternative binding paradigm for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 1214–1218 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1214 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

