Harnessing Dendritic Cells for Poly (D,L-lactide- co-glycolide) Microspheres (PLGA MS)-Mediated Anti-tumor Therapy
- PMID: 31024545
- PMCID: PMC6460768
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00707
Harnessing Dendritic Cells for Poly (D,L-lactide- co-glycolide) Microspheres (PLGA MS)-Mediated Anti-tumor Therapy
Abstract
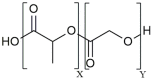
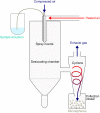
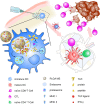
With emerging success in fighting off cancer, chronic infections, and autoimmune diseases, immunotherapy has become a promising therapeutic approach compared to conventional therapies such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunosuppressive medication. Despite the advancement of monoclonal antibody therapy against immune checkpoints, the development of safe and efficient cancer vaccine formulations still remains a pressing medical need. Anti-tumor immunotherapy requires the induction of antigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses which recognize and specifically destroy tumor cells. Due to the crucial role of dendritic cells (DCs) in initiating anti-tumor immunity, targeting tumor antigens to DCs has become auspicious in modern vaccine research. Over the last two decades, micron- or nanometer-sized particulate delivery systems encapsulating tumor antigens and immunostimulatory molecules into biodegradable polymers have shown great promise for the induction of potent, specific and long-lasting anti-tumor responses in vivo. Enhanced vaccine efficiency of the polymeric micro/nanoparticles has been attributed to controlled and continuous release of encapsulated antigens, efficient targeting of antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as DCs and subsequent induction of CTL immunity. Poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA), as one of these polymers, has been extensively studied for the design and development of particulate antigen delivery systems in cancer therapy. This review provides an overview of the current state of research on the application of PLGA microspheres (PLGA MS) as anti-tumor cancer vaccines in activating and potentiating immune responses attempting to highlight their potential in the development of cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: CTL; PLGA; anti-tumor response; cancer vaccine; dendritic cell; immunotherapy; microspheres; spray drying.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delivery of tumor antigens to dendritic cells using biodegradable microspheres.Methods Mol Med. 2005;109:35-46. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-862-5:035. Methods Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15585911
-
Targeting dendritic cells with nano-particulate PLGA cancer vaccine formulations.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011 Sep 10;63(10-11):943-55. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2011.05.021. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011. PMID: 21679733 Review.
-
PLGA nanoparticle-mediated delivery of tumor antigenic peptides elicits effective immune responses.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1475-87. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S29506. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22619507 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced stimulation of anti-breast cancer T cells responses by dendritic cells loaded with poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) nanoparticle encapsulated tumor antigens.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 26;35(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0444-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27782834 Free PMC article.
-
PLGA microspheres for improved antigen delivery to dendritic cells as cellular vaccines.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005 Jan 10;57(3):475-82. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2004.09.007. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005. PMID: 15560953 Review.
Cited by
-
Size, shape, charge and "stealthy" surface: Carrier properties affect the drug circulation time in vivo.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2021 Jul;16(4):444-458. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34703494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective efficacy of Toxoplasma gondii GRA12 or GRA7 recombinant proteins encapsulated in PLGA nanoparticles against acute Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jul 12;13:1209755. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1209755. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37502604 Free PMC article.
-
Drug delivery carriers with therapeutic functions.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Sep;176:113884. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.113884. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 34302897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intradermal Vaccination with PLGA Nanoparticles via Dissolving Microneedles and Classical Injection Needles.Pharm Res. 2024 Feb;41(2):305-319. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03665-7. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38332390 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering dendritic cell biomimetic membrane as a delivery system for tumor targeted therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 27;22(1):663. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02913-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39465376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

