Effects of Different Stressors Are Modulated by Different Neurobiological Systems: The Role of GABA-A Versus CB1 Receptor Gene Variants in Anxiety and Depression
- PMID: 31024264
- PMCID: PMC6467241
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00138
Effects of Different Stressors Are Modulated by Different Neurobiological Systems: The Role of GABA-A Versus CB1 Receptor Gene Variants in Anxiety and Depression
Abstract
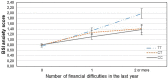
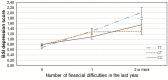
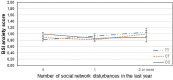
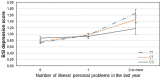
Environmental stress and its interaction with genetic variation are key contributors in the development of depression and anxiety, yet there is a failure to identify replicable genetic variants and gene-interaction effects in the background of these psychiatric symptoms. Recently it has been reported that 5-HTTLPR and NOSI interact with financial but not other types of recent stressors in the development of depression. In the present study we investigated the interaction of GABRA6 rs3219151 and CNR1 rs7766029 in interaction with different types of recent life events on the presence of depression and anxiety in a large general population sample. 2191 participants completed the List of Threatening Experiences questionnaire which covers four categories of stressful life events (financial problems, illness/personal problems, intimate relationships, and social network) experienced over the previous year and the Brief Symptom Inventory for depression and anxiety symptoms. Participants were genotyped for rs3219151 and rs7766029. Data were analyzed with linear regression models with age and gender as covariates. Results indicated that CNR1 rs7766029 interacted significantly with financial but not other types of life events both in case of depression and anxiety symptoms. In contrast, GABRA6 rs3219151 showed a significant interaction with social network related life events in case of anxiety and with illness/personal problem-related life events in case of depression. Our results suggest that the psychological impact of different types of recent stress may be differentially modulated by distinct molecular genetic pathways. Furthermore, in case of certain genetic variants, the occurring psychiatric symptom may depend on the type of stress experienced.
Keywords: CNR1; GABA; GABRA6; anxiety; depression; endocannabinoid system; gene-environment interaction; types of stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CNR1 gene is associated with high neuroticism and low agreeableness and interacts with recent negative life events to predict current depressive symptoms.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Jul;34(8):2019-27. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.19. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19242408
-
A new stress sensor and risk factor for suicide: the T allele of the functional genetic variant in the GABRA6 gene.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 10;7(1):12887. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12776-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29018204 Free PMC article.
-
Financial difficulties but not other types of recent negative life events show strong interactions with 5-HTTLPR genotype in the development of depressive symptoms.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 May 3;6(5):e798. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.57. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27138797 Free PMC article.
-
[Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a consequence of the interaction between an individual genetic susceptibility, a traumatogenic event and a social context].Encephale. 2012 Oct;38(5):373-80. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 23062450 Review. French.
-
A new clinical evidence-based gene-environment interaction model of depression.Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2012 Dec;14(4):213-20. Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2012. PMID: 23269207 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflamed Mind: Multiple Genetic Variants of IL6 Influence Suicide Risk Phenotypes in Interaction With Early and Recent Adversities in a Linkage Disequilibrium-Based Clumping Analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Oct 29;12:746206. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.746206. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34777050 Free PMC article.
-
Variation along P2RX7 interacts with early traumas on severity of anxiety suggesting a role for neuroinflammation.Sci Rep. 2023 May 12;13(1):7757. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34781-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37173368 Free PMC article.
-
A Double Hit of Social and Economic Stress in Mice Precipitates Changes in Decision-Making Strategies.Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Jul 1;96(1):67-78. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.12.011. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38141911
-
"Out, out, brief candle! Life's but a walking shadow": 5-HTTLPR Is Associated With Current Suicidal Ideation but Not With Previous Suicide Attempts and Interacts With Recent Relationship Problems.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 25;11:567. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00567. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32670107 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of sociocultural and behavioral factors into the clinical framework of cardiovascular studies in Hispanic/Latino populations: Relevance during the SARS-COV-2 pandemic.J Clin Transl Sci. 2021 Mar 8;5(1):e101. doi: 10.1017/cts.2021.20. J Clin Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34192056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal A., Nelson E. C., Littlefield A. K., Bucholz K. K., Degenhardt L., Henders A. K., et al. (2012). Cannabinoid receptor genotype moderation of the effects of childhood physical abuse on anhedonia and depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 69 732–740. 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.2273 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aleksandrova L. R., Souz R. P., Bagby M. R., Casey D. M., Hodgins D. C., Smith G. J., et al. (2012). Genetic underpinnings of neuroticism: a replication study. J. Addict. Res. Ther. 3:119 10.4172/2155-6105.1000119 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

