PID1 alters the antilipolytic action of insulin and increases lipolysis via inhibition of AKT/PKA pathway activation
- PMID: 30990811
- PMCID: PMC6467375
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214606
PID1 alters the antilipolytic action of insulin and increases lipolysis via inhibition of AKT/PKA pathway activation
Erratum in
-
Correction: PID1 alters the antilipolytic action of insulin and increases lipolysis via inhibition of AKT/PKA pathway activation.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 17;14(6):e0218721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218721. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31206557 Free PMC article.
Abstract
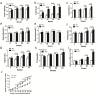
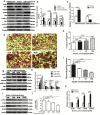
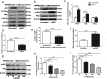
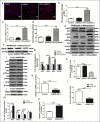
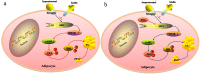
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 (PID1) on the insulin-induced activation of the AKT (protein kinase B)/protein kinase A (PKA)/hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) pathway and lipolysis.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were fed either chow or a high-fat diet (HFD). The levels of insulin, glycerol, free fatty acids (FFAs) and PID1 mRNA expression were measured in the 2 groups. Furthermore, we examined the role of PID1 in the regulation of the AKT/PKA/HSL cascade and lipolysis in the 3T3-L1 cell line.
Results: Adipose tissue from HFD rats exhibited elevated PID1 expression, which showed a positive correlation with insulin levels and lipolysis. In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, we found that the antilipolytic effect of insulin is mediated by AKT and that phosphorylated AKT results in the promotion of PDE3B expression, the dephosphorylation of PKA and HSL and the suppression of glycerol release. However, overexpression of PID1 and treatment with 1 μM isoproterenol and 100 nM insulin for 24 h resulted in an increased release of glycerol and a noticeable inhibition of AKT phosphorylation, PDE3B expression and the phosphorylation of PKA/HSL in 3T3-L1 cells. In contrast, knockdown of PID1 and treatment with the above reagents inhibited lipolysis and activated the phosphorylation of AKT, which resulted in the dephosphorylation of PKA and HSL.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that PID1 in adipose tissue increases lipolysis by altering the antilipolytic action of insulin. This suggests that PID1 may represent a new therapeutic target to ameliorate adipocyte lipolysis and hence improve insulin sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
QRFP-43 inhibits lipolysis by preventing ligand-induced complex formation between perilipin A, caveolin-1, the catalytic subunit of protein kinase and hormone-sensitive lipase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1851(5):657-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25677823
-
Differential regulation of adipocyte PDE3B in distinct membrane compartments by insulin and the beta3-adrenergic receptor agonist CL316243: effects of caveolin-1 knockdown on formation/maintenance of macromolecular signalling complexes.Biochem J. 2009 Dec 10;424(3):399-410. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090842. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19747167 Free PMC article.
-
KMUP-1, a GPCR Modulator, Attenuates Triglyceride Accumulation Involved MAPKs/Akt/PPARγ and PKA/PKG/HSL Signaling in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes.Molecules. 2018 Sep 23;23(10):2433. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102433. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30249030 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms regulating hormone-sensitive lipase and lipolysis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Dec;31(Pt 6):1120-4. doi: 10.1042/bst0311120. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 14641008 Review.
-
Update on the synergistic effect of HSL and insulin in the treatment of metabolic disorders.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep 20;10:2042018819877300. doi: 10.1177/2042018819877300. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31565213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Beneficial Effects of Essential Oils in Anti-Obesity Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 31;22(21):11832. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111832. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Ovarian Granulosa Cells Isolated during an IVF Procedure Exhibit Differential Expression of Genes Regulating Cell Division and Mitotic Spindle Formation.J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 20;8(12):2026. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122026. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31756998 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: PID1 alters the antilipolytic action of insulin and increases lipolysis via inhibition of AKT/PKA pathway activation.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 17;14(6):e0218721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218721. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31206557 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-seq reveals insights into molecular mechanisms of metabolic restoration via tryptophan supplementation in low birth weight piglet model.J Anim Sci. 2022 May 1;100(5):skac156. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac156. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35552417 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of MAMSTR Transcription Factor-Binding Sites via ChIP-Seq in Porcine Skeletal Muscle Fibroblasts.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 23;13(11):1731. doi: 10.3390/ani13111731. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37889674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmen G Y, Víctor S M. Signalling mechanisms regulating lipolysis. Cellular signaling. 2006; 18(4): 401–408. - PubMed
-
- McTernan P G, Harte A L, Anderson L A, Green A, Smith S A, Holder J, C et al. Insulin and rosiglitazone regulation of lipolysis and lipogenesis in human adipose tissue in vitro. Diabetes. 2002; 51(5): 1493–1498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

