When a Little Bit More Makes the Difference: Expression Levels of GKRP Determines the Subcellular Localization of GK in Tanycytes
- PMID: 30983961
- PMCID: PMC6449865
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00275
When a Little Bit More Makes the Difference: Expression Levels of GKRP Determines the Subcellular Localization of GK in Tanycytes
Abstract
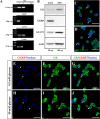
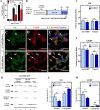
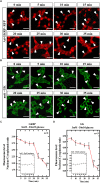
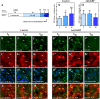
Glucose homeostasis is performed by specialized cells types that detect and respond to changes in systemic glucose concentration. Hepatocytes, β-cells and hypothalamic tanycytes are part of the glucosensor cell types, which express several proteins involved in the glucose sensing mechanism such as GLUT2, Glucokinase (GK) and Glucokinase regulatory protein (GKRP). GK catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate (G-6P), and its activity and subcellular localization are regulated by GKRP. In liver, when glucose concentration is low, GKRP binds to GK holding it in the nucleus, while the rise in glucose concentration induces a rapid export of GK from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. In contrast, hypothalamic tanycytes display inverse compartmentalization dynamic in response to glucose: a rise in the glucose concentration drives nuclear compartmentalization of GK. The underlying mechanism responsible for differential GK subcellular localization in tanycytes has not been described yet. However, it has been suggested that relative expression between GK and GKRP might play a role. To study the effects of GKRP expression levels in the subcellular localization of GK, we used insulinoma 832/13 cells and hypothalamic tanycytes to overexpress the tanycytic sequences of Gckr. By immunocytochemistry and Western blot analysis, we observed that overexpression of GKRP, independently of the cellular context, turns GK localization to a liver-like fashion, as GK is mainly localized in the nucleus in response to low glucose. Evaluating the expression levels of GKRP in relation to GK through RT-qPCR, suggest that excess of GKRP might influence the pattern of GK subcellular localization. In this sense, we propose that the low expression of GKRP (in relation to GK) observed in tanycytes is responsible, at least in part, for the compartmentalization pattern observed in this cell type. Since GKRP behaves as a GK inhibitor, the regulation of GKRP expression levels or activity in tanycytes could be used as a therapeutic target to regulate the glucosensing activity of these cells and consequently to regulate feeding behavior.
Keywords: GK regulatory protein; glucokinase; glucosensing; metabolic; tanycytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of glucokinase regulatory protein expression may contribute to low glucokinase activity in feline liver.Vet Res Commun. 2009 Mar;33(3):227-40. doi: 10.1007/s11259-008-9171-6. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Vet Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 18780155
-
Mice mutant for glucokinase regulatory protein exhibit decreased liver glucokinase: a sequestration mechanism in metabolic regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 7;96(25):14511-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14511. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10588736 Free PMC article.
-
Glial glucokinase expression in adult and post-natal development of the hypothalamic region.ASN Neuro. 2010 May 25;2(3):e00035. doi: 10.1042/AN20090059. ASN Neuro. 2010. PMID: 20531973 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Updates on Glucokinase Activators and Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Disrupters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;15(3):205-212. doi: 10.2174/1573399814666180724100749. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30039763 Review.
-
Glucokinase regulatory protein: a balancing act between glucose and lipid metabolism in NAFLD.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 29;14:1247611. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1247611. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37711901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GKRP-dependent modulation of feeding behavior by tanycyte-released monocarboxylates.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 3;12(4):1518-1536. doi: 10.7150/thno.66634. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35198055 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of KLF4 and AMPK in the inhibition of glycolysis by pulsatile shear stress in endothelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 25;118(21):e2103982118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2103982118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34001623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ainscow E. K., Mirshamsi S., Tang T., Ashford M. L. J., Rutter G. A. (2002). Dynamic imaging of free cytosolic ATP concentration during fuel sensing by rat hypothalamic neurones: evidence for ATP-independent control of ATP-sensitive K(+) channels. J. Physiol. 544 429–445. 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.022434 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

