Pixel: a content management platform for quantitative omics data
- PMID: 30944779
- PMCID: PMC6441322
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.6623
Pixel: a content management platform for quantitative omics data
Abstract
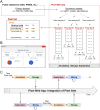
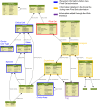
Background: In biology, high-throughput experimental technologies, also referred as "omics" technologies, are increasingly used in research laboratories. Several thousands of gene expression measurements can be obtained in a single experiment. Researchers are routinely facing the challenge to annotate, store, explore and mine all the biological information they have at their disposal. We present here the Pixel web application (Pixel Web App), an original content management platform to help people involved in a multi-omics biological project.
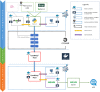
Methods: The Pixel Web App is built with open source technologies and hosted on the collaborative development platform GitHub (https://github.com/Candihub/pixel). It is written in Python using the Django framework and stores all the data in a PostgreSQL database. It is developed in the open and licensed under the BSD 3-clause license. The Pixel Web App is also heavily tested with both unit and functional tests, a strong code coverage and continuous integration provided by CircleCI. To ease the development and the deployment of the Pixel Web App, Docker and Docker Compose are used to bundle the application as well as its dependencies.
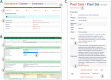
Results: The Pixel Web App offers researchers an intuitive way to annotate, store, explore and mine their multi-omics results. It can be installed on a personal computer or on a server to fit the needs of many users. In addition, anyone can enhance the application to better suit their needs, either by contributing directly on GitHub (encouraged) or by extending Pixel on their own. The Pixel Web App does not provide any computational programs to analyze the data. Still, it helps to rapidly explore and mine existing results and holds a strategic position in the management of research data.
Keywords: Data cycle analyses; Omics; Open source; Pixel Web App.
Conflict of interest statement
William Durand and Julien Maupetit are employed by TailorDev SAS. Charles Hébert is employed by Biorosetics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Scalable decision support at the point of care: a substitutable electronic health record app for monitoring medication adherence.Interact J Med Res. 2013 Jul 22;2(2):e13. doi: 10.2196/ijmr.2480. Interact J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23876796 Free PMC article.
-
ProteomeExpert: a Docker image-based web server for exploring, modeling, visualizing and mining quantitative proteomic datasets.Bioinformatics. 2021 Apr 19;37(2):273-275. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa1088. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33416829 Free PMC article.
-
Cellenium-a scalable and interactive visual analytics app for exploring multimodal single-cell data.Bioinformatics. 2023 Jun 1;39(6):btad349. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad349. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37261846 Free PMC article.
-
The START App: a web-based RNAseq analysis and visualization resource.Bioinformatics. 2017 Feb 1;33(3):447-449. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw624. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28171615 Free PMC article.
-
REALGAR: a web app of integrated respiratory omics data.Bioinformatics. 2022 Sep 15;38(18):4442-4445. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac524. Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35863045 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Software tools, databases and resources in metabolomics: updates from 2018 to 2019.Metabolomics. 2020 Mar 7;16(3):36. doi: 10.1007/s11306-020-01657-3. Metabolomics. 2020. PMID: 32146531 Review.
-
Omics Analyses: How to Navigate Through a Constant Data Deluge.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2477:457-471. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2257-5_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35524132
References
-
- Afgan E, Baker D, Van den Beek M, Blankenberg D, Bouvier D, Čech M, Chilton J, Clements D, Coraor N, Eberhard C, Grüning B, Guerler A, Hillman-Jackson J, Von Kuster G, Rasche E, Soranzo N, Turaga N, Taylor J, Nekrutenko A, Goecks J. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016;44:W3–W10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw343. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blow N. A sequencer in every lab. BioTechniques. 2013;55:284. doi: 10.2144/000114107. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

