Dynamic and Cell-Infiltratable Hydrogels as Injectable Carrier of Therapeutic Cells and Drugs for Treating Challenging Bone Defects
- PMID: 30937371
- PMCID: PMC6439455
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.8b00764
Dynamic and Cell-Infiltratable Hydrogels as Injectable Carrier of Therapeutic Cells and Drugs for Treating Challenging Bone Defects
Abstract
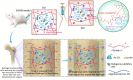
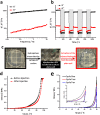
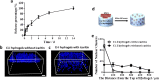
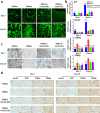
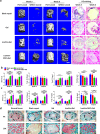
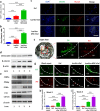
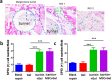
Biopolymeric hydrogels have been widely used as carriers of therapeutic cells and drugs for biomedical applications. However, most conventional hydrogels cannot be injected after gelation and do not support the infiltration of cells because of the static nature of their network structure. Here, we develop unique cell-infiltratable and injectable (Ci-I) gelatin hydrogels, which are physically cross-linked by weak and highly dynamic host-guest complexations and are further reinforced by limited chemical cross-linking for enhanced stability, and then demonstrate the outstanding properties of these Ci-I gelatin hydrogels. The highly dynamic network of Ci-I hydrogels allows injection of prefabricated hydrogels with encapsulated cells and drugs, thereby simplifying administration during surgery. Furthermore, the reversible nature of the weak host-guest cross-links enables infiltration and migration of external cells into Ci-I gelatin hydrogels, thereby promoting the participation of endogenous cells in the healing process. Our findings show that Ci-I hydrogels can mediate sustained delivery of small hydrophobic molecular drugs (e.g., icaritin) to boost differentiation of stem cells while avoiding the adverse effects (e.g., in treatment of bone necrosis) associated with high drug dosage. The injection of Ci-I hydrogels encapsulating mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and drug (icaritin) efficiently prevented the decrease in bone mineral density (BMD) and promoted in situ bone regeneration in an animal model of steroid-associated osteonecrosis (SAON) of the hip by creating the microenvironment favoring the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs, including the recruited endogenous cells. We believe that this is the first demonstration on applying injectable hydrogels as effective carriers of therapeutic cargo for treating dysfunctions in deep and enclosed anatomical sites via a minimally invasive procedure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Injectable stem cell-laden supramolecular hydrogels enhance in situ osteochondral regeneration via the sustained co-delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic chondrogenic molecules.Biomaterials. 2019 Jul;210:51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.04.031. Epub 2019 Apr 28. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 31075723
-
Mechanically resilient, injectable, and bioadhesive supramolecular gelatin hydrogels crosslinked by weak host-guest interactions assist cell infiltration and in situ tissue regeneration.Biomaterials. 2016 Sep;101:217-28. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.05.043. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27294539
-
Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenic Protein-2 Immobilized Fabrication of Magnesium Functionalized Injectable Hydrogels for Controlled-Delivery and Osteogenic Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Femoral Head Necrosis Repair.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 25;9:723789. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.723789. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34900987 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable and biodegradable hydrogels: gelation, biodegradation and biomedical applications.Chem Soc Rev. 2012 Mar 21;41(6):2193-221. doi: 10.1039/c1cs15203c. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Chem Soc Rev. 2012. PMID: 22116474 Review.
-
Stimuli-Sensitive Injectable Hydrogels Based on Polysaccharides and Their Biomedical Applications.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016 Dec;37(23):1881-1896. doi: 10.1002/marc.201600371. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016. PMID: 27753168 Review.
Cited by
-
Intra-Articular Injectable Biomaterials for Cartilage Repair and Regeneration.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Jul;13(17):e2303794. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303794. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38324655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages in epididymal adipose tissue secrete osteopontin to regulate bone homeostasis.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 20;13(1):427. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27683-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35058428 Free PMC article.
-
Two in One: Use of Divalent Manganese Ions as Both Cross-Linking and MRI Contrast Agent for Intrathecal Injection of Hydrogel-Embedded Stem Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 13;13(7):1076. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13071076. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34371767 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine promotes bone regeneration in bone tissue engineering.Chin Med. 2022 Jul 20;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00640-5. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35858928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of culture conditions on the mechanical and biological properties of engineered cartilage constructed with collagen hybrid scaffold and human mesenchymal stem cells.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019 Oct 19;30(10):119. doi: 10.1007/s10856-019-6321-z. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019. PMID: 31630248
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
