Modulators of Kv3 Potassium Channels Rescue the Auditory Function of Fragile X Mice
- PMID: 30936239
- PMCID: PMC6561694
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0839-18.2019
Modulators of Kv3 Potassium Channels Rescue the Auditory Function of Fragile X Mice
Abstract
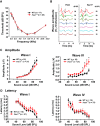
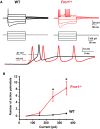
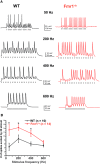
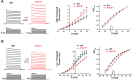
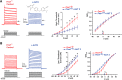
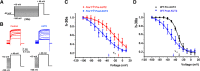
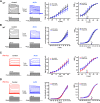
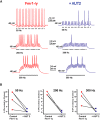
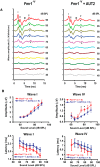
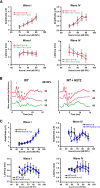
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is characterized by hypersensitivity to sensory stimuli, including environmental sounds. We compared the auditory brainstem response (ABR) recorded in vivo in mice lacking the gene (Fmr1-/y ) for fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) with that in wild-type animals. We found that ABR wave I, which represents input from the auditory nerve, is reduced in Fmr1-/y animals, but only at high sound levels. In contrast, wave IV, which represents the activity of auditory brainstem nuclei is enhanced at all sound levels, suggesting that loss of FMRP alters the central processing of auditory signals. Current-clamp recordings of neurons in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body in the auditory brainstem revealed that, in contrast to neurons from wild-type animals, sustained depolarization triggers repetitive firing rather than a single action potential. In voltage-clamp recordings, K+ currents that activate at positive potentials ("high-threshold" K+ currents), which are required for high-frequency firing and are carried primarily by Kv3.1 channels, are elevated in Fmr1-/y mice, while K+ currents that activate near the resting potential and inhibit repetitive firing are reduced. We therefore tested the effects of AUT2 [((4-({5-[(4R)-4-ethyl-2,5-dioxo-1-imidazolidinyl]-2-pyridinyl}oxy)-2-(1-methylethyl) benzonitrile], a compound that modulates Kv3.1 channels. AUT2 reduced the high-threshold K+ current and increased the low-threshold K+ currents in neurons from Fmr1-/y animals by shifting the activation of the high-threshold current to more negative potentials. This reduced the firing rate and, in vivo, restored wave IV of the ABR. Our results from animals of both sexes suggest that the modulation of the Kv3.1 channel may have potential for the treatment of sensory hypersensitivity in patients with FXS.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT mRNA encoding the Kv3.1 potassium channel was one of the first described targets of the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP). Fragile X syndrome is caused by loss of FMRP and, in humans and mice, causes hypersensitivity to auditory stimuli. We found that components of the auditory brain response (ABR) corresponding to auditory brainstem activity are enhanced in mice lacking FMRP. This is accompanied by hyperexcitability and altered potassium currents in auditory brainstem neurons. Treatment with a drug that alters the voltage dependence of Kv3.1 channels normalizes the imbalance of potassium currents, as well as ABR responses in vivo, suggesting that such compounds may be effective in treating some symptoms of fragile X syndrome.
Keywords: AUT2; auditory brainstem response; fragile X; high- and low-threshold potassium channels; medial nucleus of the trapezoid body; potassium channels.
Copyright © 2019 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein is required for rapid experience-dependent regulation of the potassium channel Kv3.1b.J Neurosci. 2010 Aug 4;30(31):10263-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1125-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20685971 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological modulators of Kv3.1 channels adjust firing patterns of auditory brain stem neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Jul 1;116(1):106-21. doi: 10.1152/jn.00174.2016. Epub 2016 Apr 6. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27052580 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of fragile X mental retardation protein in the human auditory brainstem.Neuroscience. 2014 Jul 25;273:79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 May 15. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24838064
-
Potassium channel modulation and auditory processing.Hear Res. 2011 Sep;279(1-2):32-42. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Hear Res. 2011. PMID: 21414395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensory Processing Phenotypes in Fragile X Syndrome.ASN Neuro. 2018 Jan-Dec;10:1759091418801092. doi: 10.1177/1759091418801092. ASN Neuro. 2018. PMID: 30231625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular distribution of the Fragile X mental retardation protein in the inner ear: a developmental and comparative study in the mouse, rat, gerbil, and chicken.J Comp Neurol. 2023 Jan;531(1):149-169. doi: 10.1002/cne.25420. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Comp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36222577 Free PMC article.
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein modulates somatic D-type K+ channels and action potential threshold in the mouse prefrontal cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Dec 1;124(6):1766-1773. doi: 10.1152/jn.00494.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 30. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 32997566 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated potassium channels as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Oct 1;18:1449151. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1449151. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39411003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efferent feedback controls bilateral auditory spontaneous activity.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 27;12(1):2449. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22796-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33907194 Free PMC article.
-
Interneuron Dysfunction and Inhibitory Deficits in Autism and Fragile X Syndrome.Cells. 2021 Oct 1;10(10):2610. doi: 10.3390/cells10102610. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aloisi E, Le Corf K, Dupuis J, Zhang P, Ginger M, Labrousse V, Spatuzza M, Georg Haberl M, Costa L, Shigemoto R, Tappe-Theodor A, Drago F, Vincenzo Piazza P, Mulle C, Groc L, Ciranna L, Catania MV, Frick A (2017) Altered surface mGluR5 dynamics provoke synaptic NMDAR dysfunction and cognitive defects in Fmr1 knockout mice. Nat Commun 8:1103. 10.1038/s41467-017-01191-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
